Manufacturing technology stands at the forefront of industrial progress, continuously transforming the landscape of production processes across various industries. This comprehensive guide delves into the realm of manufacturing technology, exploring its significance, advancements, and the profound impact it has on modern industries.
1. Understanding Manufacturing Technology
At its core, manufacturing technology encompasses the tools, techniques, and systems used in the production of goods. It spans a wide spectrum of processes, from traditional methods to cutting-edge technologies, including:
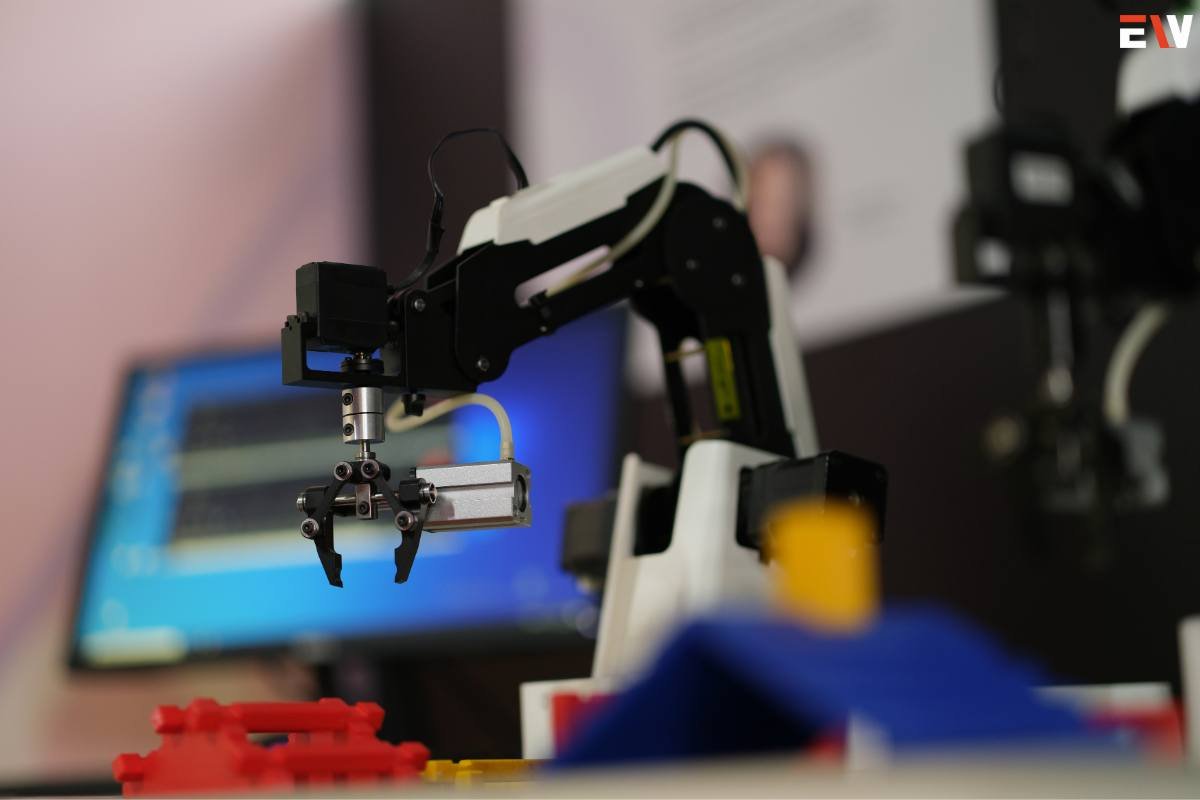
- Automation: Integration of robotics and computer-controlled systems to streamline production.
- Additive Manufacturing: Utilization of 3D printing technology to create intricate parts and prototypes.
- Advanced Materials: Development and utilization of novel materials for enhanced product performance.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Interconnectivity of devices for data exchange and process optimization.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Implementation of AI-driven systems for predictive maintenance and process optimization.
2. Impact of Manufacturing Technology
a. Efficiency and Precision:
- Advanced machinery and automated processes ensure higher precision and consistency in production, minimizing errors and rework.
b. Cost Reduction:

- Streamlined processes and optimized workflows lead to cost savings through reduced labor requirements and minimized material waste.
c. Innovation and Customization:
- Additive manufacturing enables the creation of highly customized and complex parts that were previously unattainable through conventional methods.
d. Sustainable Practices:
- Technologies like IoT and AI aid in resource optimization, reducing energy consumption and promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
3. Evolution of Manufacturing Technology
a. Industry 4.0:
- Industry 4.0 heralds the era of smart manufacturing, where interconnected systems and real-time data facilitate autonomous decision-making and process optimization.
b. Robotics and Automation:
- From automated assembly lines to collaborative robots (cobots), robotics revolutionizes manufacturing by augmenting human capabilities and improving safety.
c. Additive Manufacturing Advancements:
- Innovations in 3D printing technology allow for the creation of intricate designs, rapid prototyping, and even production of end-use parts in certain industries.
4. Key Trends Shaping Manufacturing Technology
a. Digital Twin Technology:
- Implementation of digital replicas of physical systems aids in simulation, optimization, and predictive maintenance.
b. Edge Computing and Cloud Integration:
- Edge computing and cloud solutions enhance connectivity and data accessibility, enabling real-time decision-making and remote monitoring.
c. Cybersecurity in Manufacturing:
- Heightened focus on cybersecurity measures to protect interconnected systems from potential cyber threats and data breaches.
5. Future Prospects and Innovations
a. Nanotechnology and Materials Science:
- Advancements in nanotechnology enable the development of lighter, stronger materials with diverse applications in manufacturing.
b. Sustainable Practices and Circular Economy:
- Embracing circular economy principles leads to the reutilization of materials, reducing waste and environmental impact.
c. Human-Machine Collaboration:
- Continued advancements in AI and robotics facilitate enhanced collaboration between humans and machines, optimizing efficiency and productivity.
6. The Role of Education and Skill Development

As manufacturing technology evolves, the need for skilled professionals proficient in handling these advanced technologies becomes imperative. Investing in education and skill development programs equips the workforce to adapt to these technological shifts and ensures continued innovation in the manufacturing sector.
7. Supply Chain Optimization:
- Predictive Analytics: Leveraging data analytics and AI for predictive analysis aids in optimizing supply chain operations, reducing lead times, and minimizing inventory costs.
- Blockchain Integration: Implementing blockchain technology ensures transparency and traceability across the supply chain, preventing counterfeit products and enhancing trust among stakeholders.
8. Personalized Production and Mass Customization:
- Customer-Centric Approach: Technologies like additive manufacturing allow for the production of personalized products tailored to individual customer needs and preferences.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: Facilitating on-demand production reduces inventory stockpiles, minimizing waste and enabling companies to respond quickly to market demands.
9. Regulatory Compliance and Standards:
- Adherence to Standards: Compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards ensures product quality, safety, and conformity to global benchmarks.
- Ethical Manufacturing Practices: Embracing ethical manufacturing practices, such as sustainable sourcing and fair labor conditions, aligns with consumer preferences and regulatory requirements.
10. Collaborative Ecosystems and Partnerships:
- Open Innovation: Collaborating with external partners, including suppliers, academia, and startups, fosters innovation and accelerates the adoption of emerging technologies.
- Technology Transfer and Knowledge Sharing: Establishing platforms for technology transfer and knowledge sharing within industry ecosystems enhances collective capabilities and accelerates advancements.
11. Resilience and Risk Mitigation:
- Disaster Preparedness: Implementing resilient manufacturing systems capable of withstanding disruptions, such as natural disasters or supply chain disruptions, ensures business continuity.
- Diversification Strategies: Diversifying sourcing locations and suppliers mitigates risks associated with geopolitical or economic uncertainties.
12. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Integration:
- Enhanced Training and Maintenance: AR and VR technologies facilitate immersive training experiences for employees and aid in the maintenance and troubleshooting of complex machinery.
- Design and Prototyping: Leveraging AR and VR for design visualization and prototyping accelerates the product development lifecycle and improves design accuracy.
13. Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Smart Factories:

- Real-Time Data Analytics: IIoT enables the collection of real-time data from machinery and equipment, empowering informed decision-making and predictive maintenance.
- Autonomous Manufacturing: Smart factories leverage IIoT, AI, and robotics to achieve higher levels of automation and efficiency in production processes.
14. Industry-Specific Applications:
- Healthcare Technology: Innovations in manufacturing technology enable the production of custom medical devices, prosthetics, and pharmaceuticals, revolutionizing healthcare.
- Automotive and Aerospace Innovations: Advanced manufacturing technologies enhance vehicle design, materials, and production processes, contributing to lighter and more fuel-efficient vehicles and aircraft.
Conclusion:
The landscape of manufacturing technology encompasses a myriad of innovations and strategies that continue to redefine industrial practices. By embracing a holistic approach, integrating cutting-edge technologies, and fostering collaborative ecosystems, industries can not only optimize their operations but also contribute to a sustainable, resilient, and technologically advanced future.
As manufacturing technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for innovation and progress are boundless, offering a pathway to enhanced efficiency, product customization, and sustainable practices across diverse industries.