Sheet metal fabrication, SMF, is a centuries-old craft that has evolved into a sophisticated process, vital across industries. From aerospace to automotive, construction to manufacturing, sheet metal fabrication plays a pivotal role in creating durable, functional, and intricate structures and components.
Understanding Sheet Metal Fabrication
At its core, sheet metal fabrication involves transforming flat sheets of metal into specific shapes and forms through cutting, bending, and assembling techniques. Materials commonly used include stainless steel, aluminum, brass, copper, and various alloys. The process begins with the selection of the raw material, followed by precise measurements and design considerations.
Tools of the Trade
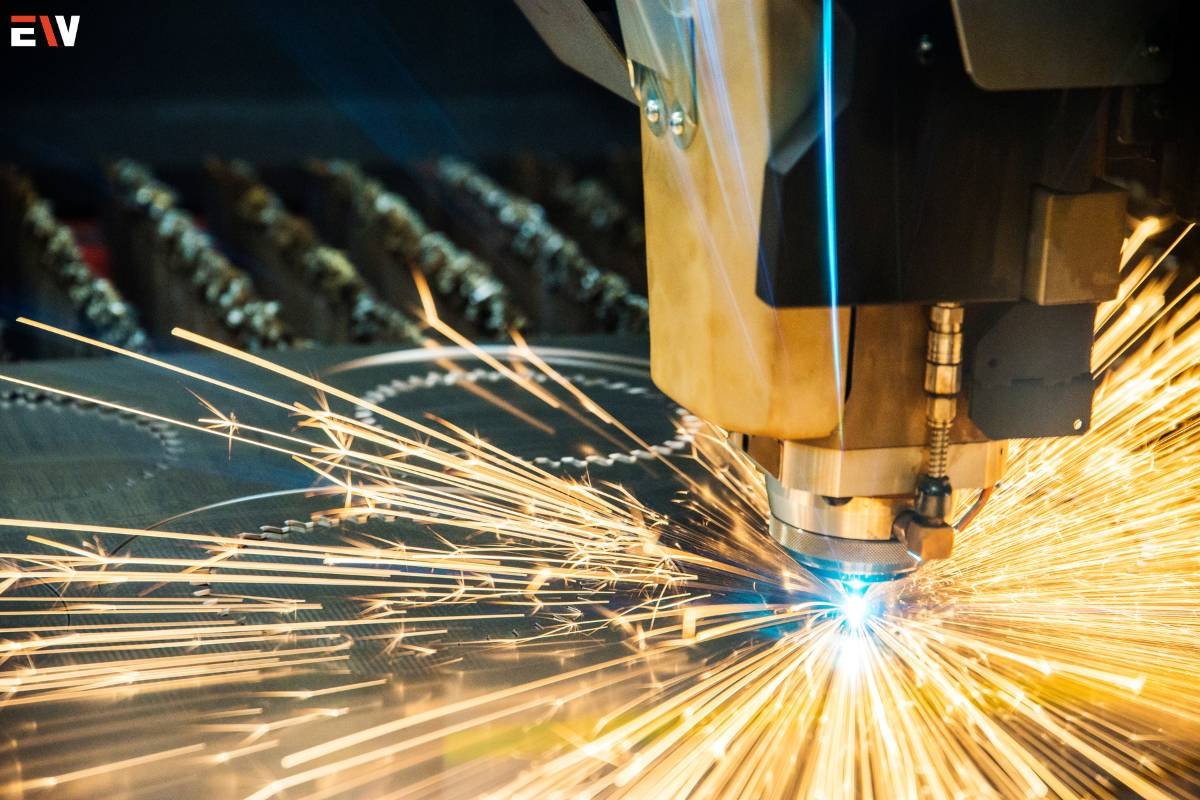
1. Shears and Cutting Tools: Shears, laser cutters, or water jets are used to cut the metal into desired shapes and sizes. Laser cutting, in particular, offers precision and versatility, enabling intricate designs and complex cuts.
2. Press Brakes: These machines bend the metal to create angles, curves, and shapes according to design specifications. They are pivotal for forming the metal accurately.
3. Roll Forming Equipment: Utilized for shaping long strips of metal into curved or cylindrical shapes, roll forming machines are essential for producing components like pipes, tubes, and curved panels.
4. Welding and Joining Tools: TIG, MIG, and spot welding equipment are used to join metal pieces together, ensuring structural integrity and durability.
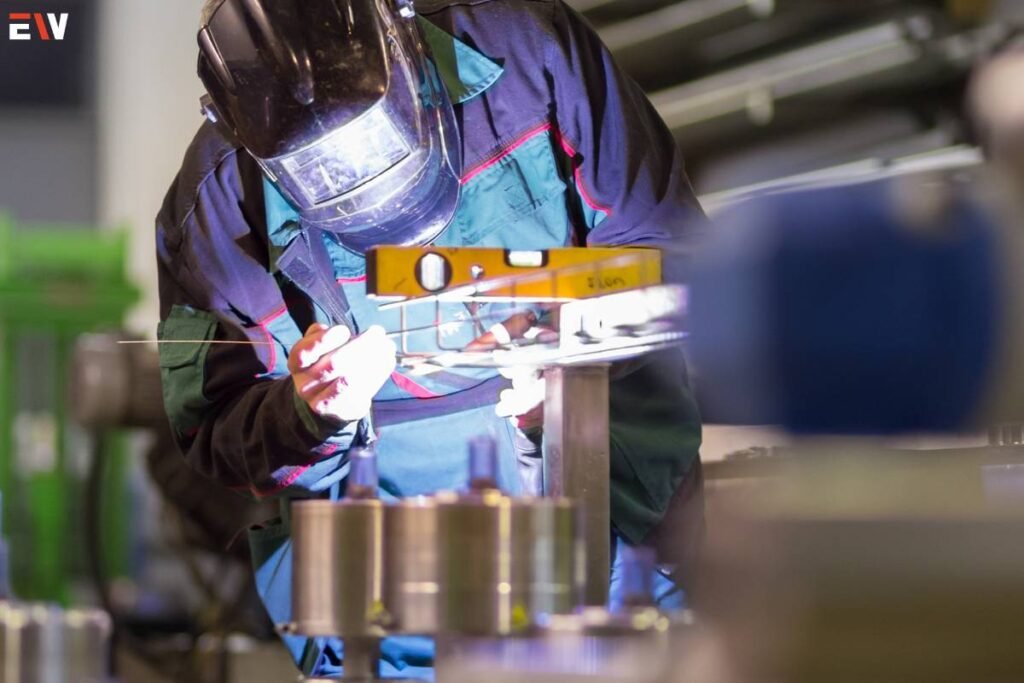

5. Finishing Tools: Grinding, sanding, and polishing equipment gives the fabricated metal its final surface finish, enhancing aesthetics and removing imperfections.
Techniques in Sheet Metal Fabrication
1. Cutting: Precision cutting is fundamental. Laser cutting and plasma cutting offer accuracy and speed, ensuring clean and smooth edges without material deformation.
2. Bending: This involves using press brakes to shape the metal. Accurate bending angles are crucial for the functionality and aesthetics of the final product.
3. Forming: Techniques like roll forming, stretching, and deep drawing shape the metal into complex geometries, catering to diverse industrial needs.
4. Joining: Welding, soldering, and fastening methods are employed to join metal pieces securely, maintaining structural integrity.
Applications Across Industries
1. Automotive: From chassis components to body panels, SMF is integral to automotive manufacturing, ensuring both safety and aesthetics.
2. Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, precision and lightweight materials are crucial. SMF creates components for aircraft, satellites, and spacecraft.
3. Construction: Architectural structures, HVAC systems, and decorative elements rely on SMF for durability and customized designs.
4. Manufacturing: Machinery, appliances, and consumer goods often incorporate fabricated sheet metal parts for their strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Innovations and Future Trends
Recent advancements in technology, such as 3D printing of metal components and the integration of AI-driven design and manufacturing processes, are revolutionizing SMF Additive manufacturing techniques offer increased design flexibility and reduced material waste, while AI optimization enhances precision and efficiency in production.
Challenges and Sustainability
The sheet metal fabrication industry faces challenges in reducing material waste, energy consumption, and environmental impact. However, efforts are underway to adopt sustainable practices, including recycling scrap metal, using eco-friendly coatings, and optimizing manufacturing processes for reduced energy consumption.
Specialized Techniques
1. Embossing and Coining: These techniques involve creating raised or sunken designs on the metal surface, adding texture or branding elements to the fabricated parts.
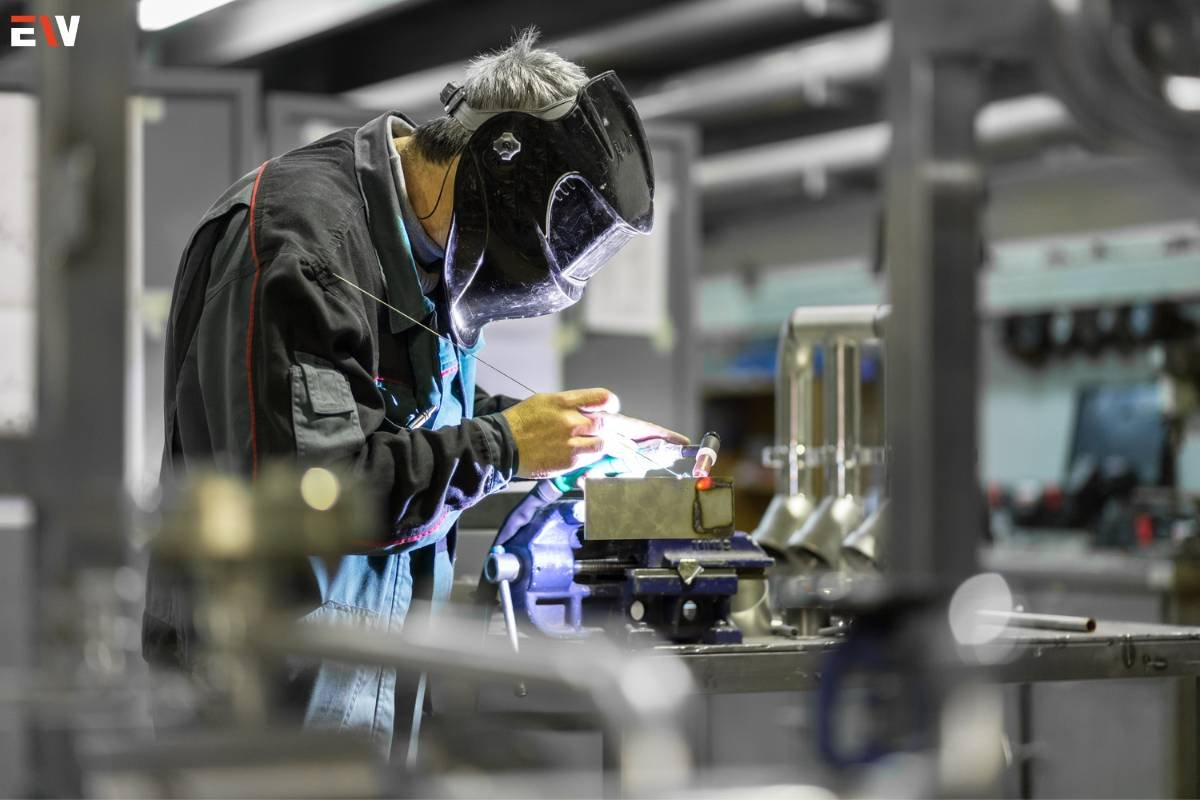

2. Piercing and Perforating: Used to create holes or patterns in the metal, these techniques are crucial for ventilation, drainage, or aesthetic purposes.
3. Hydroforming: This method uses high-pressure fluid to shape metal sheets into complex forms, offering advantages in producing lightweight yet durable components.
Quality Control and Precision
Ensuring quality throughout the fabrication process is essential. Metrology tools like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) and optical inspection systems verify dimensions and tolerances, maintaining high standards in the produced parts.
Design Considerations
SMF heavily relies on meticulous design. Factors such as material selection, thickness, bend radii, and nesting techniques are crucial for optimizing efficiency and minimizing material waste.
Customization and Prototyping
The flexibility of sheet metal fabrication allows for customization, enabling rapid prototyping and iterative design improvements. This agility is invaluable in product development and innovation.
Importance of Skilled Labor
Skilled artisans and technicians play a critical role in sheet metal fabrication. Their expertise in interpreting blueprints, operating machinery, and problem-solving contributes significantly to the quality of the final product.
Global Impact and Market Trends
The global SMF market continues to expand, driven by demand across industries. Emerging economies, technological advancements, and the adoption of automation are influencing market growth and innovation in fabrication processes.
Collaboration and Integration
Collaboration between designers, engineers, and fabricators is essential for a seamless and efficient fabrication process. Integration of CAD/CAM software allows for streamlined communication and data transfer, reducing errors and improving overall productivity.
Future Challenges and Opportunities
As technology evolves, the industry faces challenges in adapting to automation and upskilling the workforce. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation, efficiency improvements, and the development of new materials and processes.
Global Sustainability Efforts

The sheet metal fabrication industry is increasingly embracing sustainable practices. Initiatives like using recycled materials, adopting energy-efficient machinery, and exploring alternative materials contribute to reducing the environmental footprint of fabrication processes.
Conclusion
Sheet metal fabrication stands at the intersection of craftsmanship, technology, and innovation. As industries continue to evolve and demand for intricate, durable, and sustainable components grows, the art of SMF will undoubtedly continue to play a pivotal role in shaping our technological landscape. Through a blend of traditional expertise and cutting-edge advancements, this field remains integral in transforming raw metal into functional works of art that power various sectors worldwide.