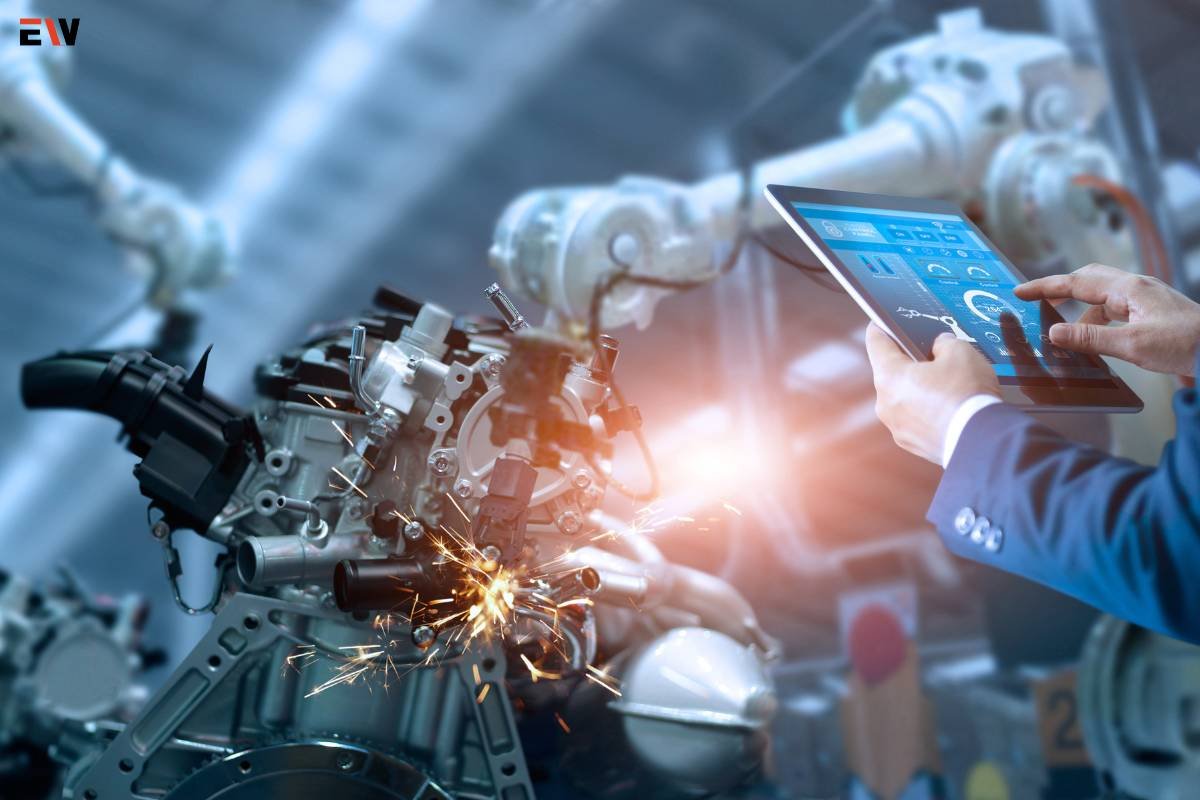
The integration of robotics in manufacturing processes has ushered in a new era of efficiency, precision, and innovation. The infusion of robotic technology into traditional manufacturing workflows has not only redefined productivity but has also fundamentally transformed the way industries operate. This seismic shift towards automated systems in manufacturing holds the promise of revolutionizing production methodologies and unlocking unprecedented levels of performance.
The Role of Robotics in Manufacturing
- Enhanced Efficiency and Precision
Robotics in manufacturing brings forth a level of efficiency and precision that surpasses human capabilities. Automated systems perform repetitive tasks with consistency and accuracy, significantly reducing errors and increasing overall productivity. This precision is particularly crucial in sectors demanding intricate and high-tolerance operations.
- Streamlined Production Processes
Integrating robotics streamlines manufacturing workflows. From assembly lines to packaging, robots can handle a diverse range of tasks swiftly and seamlessly. This optimization minimizes downtime, accelerates production cycles, and ensures a smoother, more synchronized operational flow.
- Safety and Risk Mitigation
Robotic systems contribute to a safer working environment by handling hazardous tasks, thereby reducing the risk of workplace accidents. By delegating high-risk operations to robots, manufacturers prioritize employee safety while maintaining stringent quality standards.
Impact on Manufacturing Industries
- Increased Output and Consistency
The implementation of robotics translates to heightened production output and consistency. Robots work tirelessly round the clock, maintaining a consistent level of performance without succumbing to fatigue or variability. This reliability in output strengthens supply chains and meets growing market demands.
- Customization and Flexibility
Contrary to traditional manufacturing methods, robotics allows for greater customization and flexibility in production. Adaptive robotics systems can swiftly reconfigure and adapt to varying production needs, enabling manufacturers to cater to diverse product specifications and market demands.
- Skilled Workforce and Human-Robot Collaboration

The integration of robotics doesn’t replace the workforce but complements it. Collaborative robots (cobots) work alongside humans, augmenting their capabilities and allowing employees to focus on higher-value tasks that require creativity, problem-solving, and complex decision-making.
The Future Landscape of Manufacturing
- Technological Advancements and Innovation
The future of manufacturing is deeply intertwined with continuous technological advancements in robotics. From machine learning algorithms enabling predictive maintenance to the evolution of autonomous robots, the landscape will witness a surge in innovative solutions that further optimize manufacturing processes.
- Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Robotics in manufacturing aligns with sustainability goals by optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste. Efficient production processes enabled by robotics contribute to a more sustainable industry by reducing energy consumption and environmental impact.
- Global Competitiveness and Economic Growth
The adoption of robotics bolsters a nation’s competitiveness in the global market. Countries investing in advanced manufacturing technologies position themselves as leaders, fostering economic growth, and attracting investment in high-tech industries.
- Data-Driven Decision Making

Robotics in manufacturing generates a wealth of data that can be leveraged for informed decision-making. Sensors embedded in robotic systems gather real-time information on production metrics, enabling manufacturers to analyze performance, identify bottlenecks, and optimize processes for maximum efficiency.
- Supply Chain Integration and Logistics
The integration of robotics extends beyond the factory floor and into supply chain logistics. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and drones streamline material handling and logistics, ensuring seamless movement of goods within and between manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and distribution centers.
- Remote Operations and Connectivity
Advancements in robotics technology facilitate remote monitoring and control of manufacturing processes. Through connectivity and the Internet of Things (IoT), manufacturers can oversee operations, troubleshoot issues, and make real-time adjustments, enabling a level of remote management and predictive maintenance previously unattainable.
- Regulatory Compliance and Quality Assurance
Robotic systems adhere rigorously to predefined quality standards and regulations. This adherence ensures consistent quality in manufacturing output, reducing defects and ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards, thereby enhancing product reliability and customer satisfaction.
- Economic Implications and Job Evolution
While the adoption of robotics streamlines processes and boosts efficiency, it also sparks discussions about its impact on employment. Contrary to displacing jobs entirely, the evolution of manufacturing jobs involves upskilling the workforce to operate, maintain, and program these sophisticated systems, leading to the emergence of new job roles and skill sets.
- Affordability and Accessibility

Advancements in robotics technology have made it more accessible to a broader range of manufacturing enterprises. The decreasing costs of robotic systems, coupled with modular and scalable solutions, make robotics integration more feasible for small and medium-sized manufacturers, leveling the playing field in the industry.
- Ethical Considerations and Responsible Implementation
As robotics becomes more pervasive in manufacturing, ethical considerations surrounding AI ethics, data privacy, and the ethical treatment of technology in workplaces come to the forefront. Responsible implementation involves ethical frameworks and guidelines to ensure the ethical and fair use of robotic systems.
Summing Up
The integration of robotics in manufacturing is not just a technological advancement but a transformative force reshaping the industry’s landscape. From heightened efficiency and precision to fostering innovation and reshaping workforce dynamics, the impact of robotics extends far beyond the assembly line. Embracing this technological evolution allows manufacturers to stay at the forefront of innovation, driving competitive advantage and shaping a future where human ingenuity and robotic precision converge for unparalleled advancements in manufacturing.