Think of a fortress with one gate; a breach there compromises the entire structure. This is exactly what the current identity verification model is. Today, businesses need a decentralized, tamper-proof alternative. A solution that distributes control and cryptographically seals identities.
A business’s identity is essential for trust, transactions, and compliance. As traditional security walls crumble under sophisticated attacks, the necessity for an ironclad digital passport becomes central. This is where blockchain identity management (BIM) comes into the picture.
We must beg the question: Could this be the definitive solution? Could this shift from a fragile lock-and-key system to a master key be the answer to all your problems? Read on to find out if decentralized identity management holds the key to future business security.
What is Blockchain Identity Management, and how does it work?
Before we continue, let’s understand what blockchain or decentralized identity management is.
BIM is a decentralized, cryptographically secure system. It is used for creating, storing, and verifying digital identities.
According to Identity.com, “Blockchain identity management is a decentralized approach to creating, storing, and managing digital identities using blockchain technology.”
Your digital identity is like a suitcase filled with all your important documents. Now, traditionally, in the centralized system, you hand your entire suitcase to a single, central “Hotel Registration Desk.”
The desk then holds a copy of everything, and a hacker only needs to break into that one desk to steal all the suitcases.
Now, in the BIM system, you keep the suitcase to yourself. The system operates like a vast, unchangeable Global Notary Public (the blockchain). The system only records verifiable stamps (credentials).
When a “Verifying Agent” asks for proof of your credentials, you don’t hand over your suitcase. Instead, you show them a cryptographically sealed badge for just the required information.
When a “Verifying Agent” asks for proof of your credentials, you don’t hand over your suitcase. Instead, you show them a cryptographically sealed badge for just the required information.
This setup ensures that businesses only see the minimum necessary information. Since no single entity holds all the suitcases, the system is fundamentally more secure against large-scale theft.
5 Types of Blockchain Identity You Should Know About
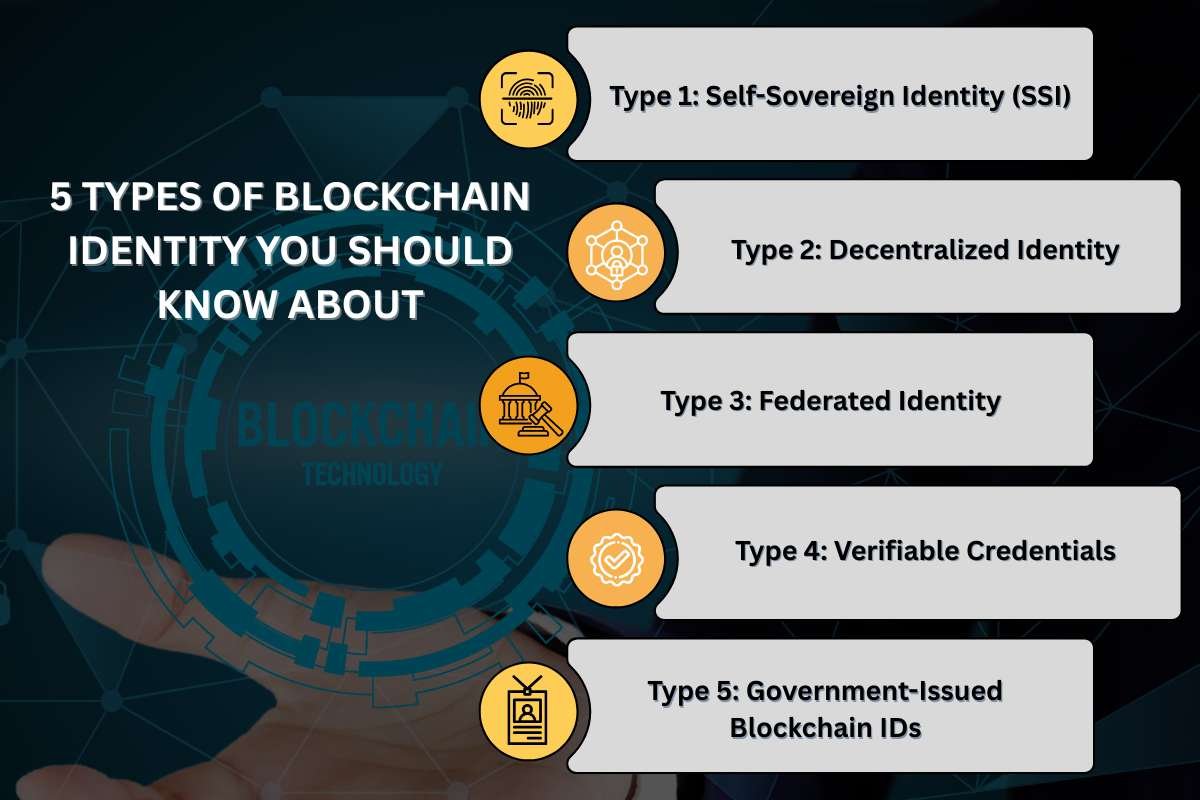
There are five types of blockchain identity verification systems. Each of them has a different purpose and functional system.
Here’s what they are:
Type 1: Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
In SSI, individuals fully control and manage their own identity data stored on the blockchain. Users decide when and with whom to share their data. Blockchain’s role is to ensure security and immutability. No intermediaries are needed for verification, empowering user privacy and autonomy.
Type 2: Decentralized Identity
Decentralized identity systems remove any central controlling authority. Identity data is stored on a blockchain. It allows users to access multiple services using a single blockchain-based identity. User data remains private and secure, shared only with consent.
Type 3: Federated Identity
Federated identity lets a user use a single digital identity across many platforms. Personal data becomes decentralized, meaning no central authority controls it. This structure is good for security and privacy compared to older login methods.
Type 4: Verifiable Credentials
Verifiable credentials are blockchain-stored digital attestations. The users can share these documents to prove identity or qualifications. These credentials are tamper-proof and independently verifiable without direct issuer involvement.
Type 5: Government-Issued Blockchain IDs
Certain governments are now using blockchain to issue digital IDs. These IDs are stored securely on the decentralized ledger. This makes them easily verifiable and highly resistant to fraud.
Seven Silent Pillars Behind Blockchain Identity Management
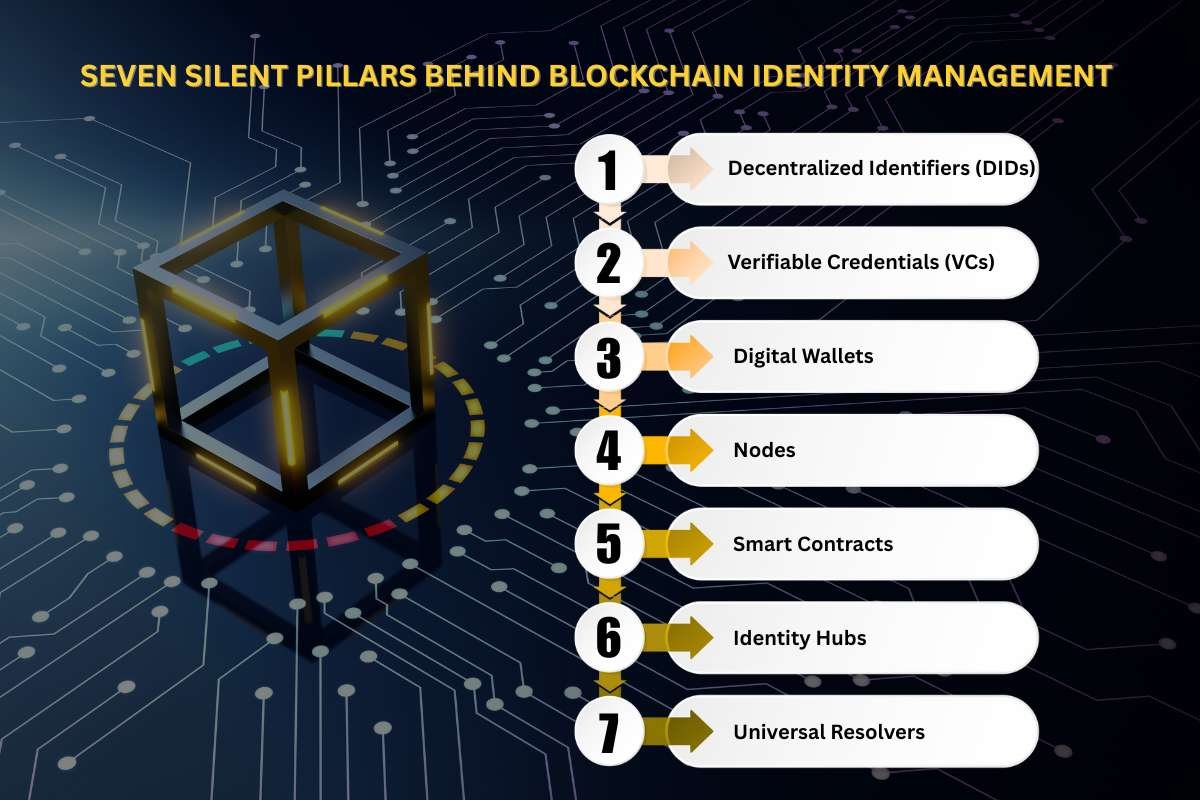
There are seven key components of BIMt. Here’s what they are:
1. Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)
Think of a DID as your username and address on the blockchain. It’s a unique digital ID that you control completely—no company or government can take it away or change it. It’s the secure foundation for your entire digital identity.
2. Verifiable Credentials (VCs)
These are your tamper-proof digital documents. Important papers include a certified degree, a driver’s license, or a passport. Trusted organizations issue them, but you store them. They are cryptographically signed, so any business can instantly verify their authenticity. This removes the need to call the original issuer.
3. Digital Wallets
This is the secure app where you keep your private keys and all your Verifiable Credentials. It’s like your actual wallet for digital IDs, letting you choose exactly what proof you share and with whom.
4. Nodes
These are the many computers that run the blockchain network. They work together to validate and store all the identity transaction data. This is what makes the system decentralized. This prevents any single point of failure and keeps all records secure.
5. Smart Contracts
These are automated programs on the blockchain that handle identity tasks. It automatically verifies a credential and enforces a rule. They execute transparently and securely without needing a human intermediary.
6. Identity Hubs
A secure personal storage area linked to your DID. This is where you manage the data associated with your identity. Here, you control who has permission to view or access it.
7. Universal Resolvers
These are services that allow different blockchain identity systems to “talk to each other.” They ensure that your DID can be verified and used seamlessly. And that too, regardless of which specific blockchain network a platform is using.
And these are the seven key components of blockchain identity management. Now, let’s move on and take a look at some real-life applications of BIM technology.
Real-world Examples Proving Blockchain Identity Systems Are Transforming Every Industry

Blockchain identity systems have applications in almost every industry. It is used in banking, healthcare, government, education, and enterprise.
In banking, it is used to streamline ‘Know Your Customer’ (KYC) and ‘Anti-Money Laundering’ (AML) processes. They allow users to share verifiable identity credentials instantly. This reduces repetitive document submissions and accelerates onboarding.
In healthcare, it secures and interoperates patient records with user-controlled verifiable credentials. The system facilitates selective sharing of health data with providers while complying with privacy laws like HIPAA.
Governments use BIM to power digital voting systems with secure, tamper-proof identities. The system is used to reduce voter fraud and ensure election integrity. It simplifies authentication for accessing government benefits and services. In the governing sphere, blockchain identity management streamlines bureaucracy.
The Upsides and Cons of the Blockchain Identity Verification System:
There are a few plus points of BIM technology, but it also has downsides that come along with it.
Here’s what they are:
| Aspect | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Control & Ownership | Users have full control over their data, eliminating centralized risks. | Users may resist new models and need education for adoption. |
| Security & Privacy | Cryptography and decentralization protect against breaches and tampering. | Privacy management is complex; zero-knowledge proofs add technical overhead. |
| Fraud Prevention | Verifiable credentials reduce identity theft and forgery. | Legal and regulatory uncertainty can limit deployment confidence. |
| Verification Efficiency | Smart contracts enable instant, low-cost verification. | Integration with legacy systems is technically demanding. |
| Interoperability | DIDs allow use across platforms without repeated verification. | Lack of unified global standards hinders seamless interoperability. |
| Transparency & Compliance | Immutable audit trails enhance trust and regulatory compliance. | Scalability limits may increase costs and slow response times. |
Future Trends and Market Analysis

A report by global market research predicted the BIM market to grow from $2.8 billion in 2024 to $4.91 billion in 2025. It is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 75.2%
According to Future Market Insights, the blockchain identity management market is estimated to be valued at USD 7.6 billion in 2025. The market is projected to reach USD 438.5 billion by 2035. It shows a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 50.0% over the forecast period.
North America currently dominates the market, holding a 42.73% share. The dominance is due to early adoption, advanced infrastructure, and regulatory support.
This fast growth is due to the increasing cybersecurity threats, privacy regulations, and the need for decentralized secure identity verification across industries such as finance, healthcare, and public services.
Adoption is also spiking in emerging markets like India and China. The Indian market is expected to grow at a 62.5% CAGR between 2025 and 2035. The Chinese market is at the forefront with a 67.5% CAGR by 2035.
Also read: Navigating the Future: A Comprehensive Exploration of Emerging Technologies
Conclusion:
We began by questioning whether a definitive solution exists for the digital identity crisis. The evidence overwhelmingly confirms that the traditional lock-and-key model is archaic. The shift toward a decentralized framework is a necessity for modern enterprise security. Blockchain identity management offers the required cryptographic sealing and user control that centralized systems fundamentally lack.
The projected market growth, driven by urgent needs across finance and healthcare, validates this trajectory. Businesses must embrace these self-sovereign models to future-proof their operations against escalating cyber threats and tightening privacy laws. A distributed network is the only defense against a single point of failure. Yes, blockchain identity management is the key to future business security.
FAQs
1. Is the user’s personal data actually stored on the public blockchain?
The sensitive personal data is not stored on the blockchain. Only a cryptographic hash of the Verifiable Credential is recorded to prove its authenticity and immutability.
2. What is the main legal challenge to widespread adoption?
A key challenge is regulatory uncertainty and ensuring compliance with existing global data protection laws like GDPR’s “right to be forgotten,” which conflicts with the blockchain’s immutable nature.
3. Which specific industries are currently leading the adoption of blockchain identity management technology?
Financial services, healthcare, and governments are leading the early commercial and pilot adoption.