At 2:17 a.m., a water pipe beneath a quiet Midwestern street senses a pressure difference. It doesn’t burst. It doesn’t flood homes. Instead, it sends a silent alert, triggering a repair order before residents ever wake up. This is a primary example of using IoT to build resilient infrastructure—a city fixing a problem before it becomes a crisis.
This is what resilience looks like in the age of the Internet of Things, and by 2026, it may be the difference between cities that endure and cities that fracture.
Across the United States, cities are learning a new language, one spoken by sensors embedded in bridges, algorithms regulating traffic lights, and data platforms predicting failures days or even months in advance. Infrastructure, once static and reactive, is becoming perceptive and anticipatory. Roads feel congested before gridlock sets in. Power systems sense strain before outages ripple through neighborhoods. Flood defenses respond to rainfall in real time, not hindsight.
The shift is subtle but profound. These cities are no longer waiting for systems to break to prove they were under pressure. They are listening continuously, intelligently, and at scale. And in a world where climate shocks, population growth, and aging infrastructure collide, that ability to listen before reacting may be the most powerful upgrade urban America has ever made.
The Strategic Foundation: Real-Time Visibility and Data Integration
Urban resilience today begins with a city that can sense itself. Thousands of embedded Internet of Things sensors turn roads, grids, pipes, and structures into a living digital nervous system streaming real-time signals to shared dashboards instead of dusty control rooms. Decisions shift from hindsight to instant insight.
Los Angeles brings this to life through its ATSAC system. With 40,000 detectors across 4,500 intersections, traffic lights think, learn, and adapt in real time. Machine learning fine-tunes signals every second, cutting average travel times by 10% saving fuel, reducing emissions, and reclaiming hours from daily commutes.
Water Infrastructure: From Reactive Repair to Predictive Maintenance
Water infrastructure rarely makes headlines until it fails. Yet beneath city streets, invisible leaks quietly drain billions of dollars and millions of gallons each year. With nearly 30% of the global water supply lost as non-revenue water, using IoT to build resilient infrastructure has emerged as a critical strategy for accountability, turning blind networks into systems that listen, learn, and respond.
Chicago offers a powerful proof point. By installing acoustic sensors that “hear” the faint signatures of leaking pipes, the city cut water loss by 16% unlocking $15 million in annual savings while preventing future damage.
In San Francisco, the focus shifted from streets to skyscrapers. A high-rise once plagued by $12 million in water damage deployed LoRa-enabled sensors to continuously monitor pipe health, transforming risk into real-time visibility and early intervention.
Energy Resilience Through Distributed Monitoring and Adaptive Control
Centralized power grids were built to deliver electricity, not anticipate stress. IoT-enabled smart grids change that equation. With distributed sensors, real-time data, and automated controls, energy systems can now see demand as it forms, balance loads instantly, and respond before outages ripple outward.
Cities are already proving the payoff. Los Angeles’ digitally connected LED streetlights save $3 million annually while adjusting brightness by time and activity. Portland cut lighting costs by 35% without compromising safety. Together with demand-response programs, smart grids turn energy from a fragile utility into a resilient, adaptive network.
Transportation Networks: Congestion Reduction and Emergency Response
Intelligent transportation systems driven by IoT sensors and connected infrastructure improve mobility efficiency while reducing emissions and enhancing emergency response capabilities. Columbus, Ohio, has equipped over 600 municipal vehicles, including buses and emergency vehicles, with vehicle-to-infrastructure communication technology that automatically adjusts traffic signal timing when emergency vehicles approach intersections. This system reduced emergency response times by 15%, a metric with direct implications for survival outcomes in medical emergencies and fire response scenarios.
The same city deployed connected vehicle technology at 85 intersections, resulting in a 17% reduction in travel times and a 12% reduction in emissions compared to conventional traffic management. San Francisco’s AI-driven traffic management system, which processes data from over 30,000 IoT sensors, has improved the transit system’s on-time performance from 72% to 94% since 2022 through optimized scheduling and routing informed by real-time demand patterns.
Natural Disaster Preparedness: Early Warning and Automated Response

Using IoT to build resilient infrastructure enables cities to move beyond post-disaster response to pre-disaster anticipation and prevention. San Francisco has deployed thousands of seismic sensors integrated with AI-powered analysis systems that can provide approximately 15 seconds of warning before earthquake shaking reaches the city. This seemingly brief window of time enables critical automated interventions: BART trains automatically slow to reduce derailment risk, fire station doors unlock to facilitate rapid vehicle deployment, and building systems initiate protective measures. Water level sensors and flood monitoring networks provide municipalities with real-time hydrological data necessary for flood prediction and early evacuation warnings.
Structural Health Monitoring and Infrastructure Longevity
Predictive maintenance is where IoT delivers its quietest and most valuable wins. Instead of fixing infrastructure too early or too late, cities now listen to it. Sensors woven into bridges, tunnels, pipelines, and buildings track stress, vibration, heat, and pressure in real time, spotting trouble long before breakdown surface.
According to McKinsey, this approach cuts maintenance costs by 30% and extends asset life by 20%. Cities like Tokyo and Barcelona use AI-driven analytics to predict failures precisely, servicing assets at the right moment, not after disruption strikes.
Data-Driven Resource Allocation and Service Delivery
IoT infrastructure generates enormous volumes of data that, when properly analyzed, enable cities to optimize resource allocation across departments. Los Angeles reported an 82% reduction in “Not Clean” streets within a single year by applying data analytics to street condition monitoring, enabling sanitation resources to target areas with genuine need rather than following fixed routes regardless of actual conditions.
Boston’s “Streets Lab” program uses over 300 pedestrian counting sensors to measure how residents actually use public spaces, providing data that informs park and streetscape redesign decisions. This data-driven approach increased utilization of public areas by 28% while improving accessibility for residents with disabilities.
Implementation Framework and Governance

Successful IoT deployment in cities requires institutional frameworks that address standardization, interoperability, privacy, and cybersecurity. New York City’s comprehensive strategy for using IoT to build resilient infrastructure establishes governance structures that coordinate wireless communications deployments, maintain citywide device inventories, and establish standardized review processes for sharing data across city agencies while protecting citizen privacy.
Los Angeles’s SmartLA 2028 initiative explicitly addresses the challenge of sensor proliferation by requiring the adoption of an IoT shared usage policy that prevents redundant sensor networks from congesting the urban environment while establishing public-private partnerships for open-source IoT integration platforms. This governance approach recognizes that IoT infrastructure represents a long-term municipal asset requiring coordination across departments, private sector partners, and citizen stakeholders.
Quantified Outcomes and Municipal Benefits
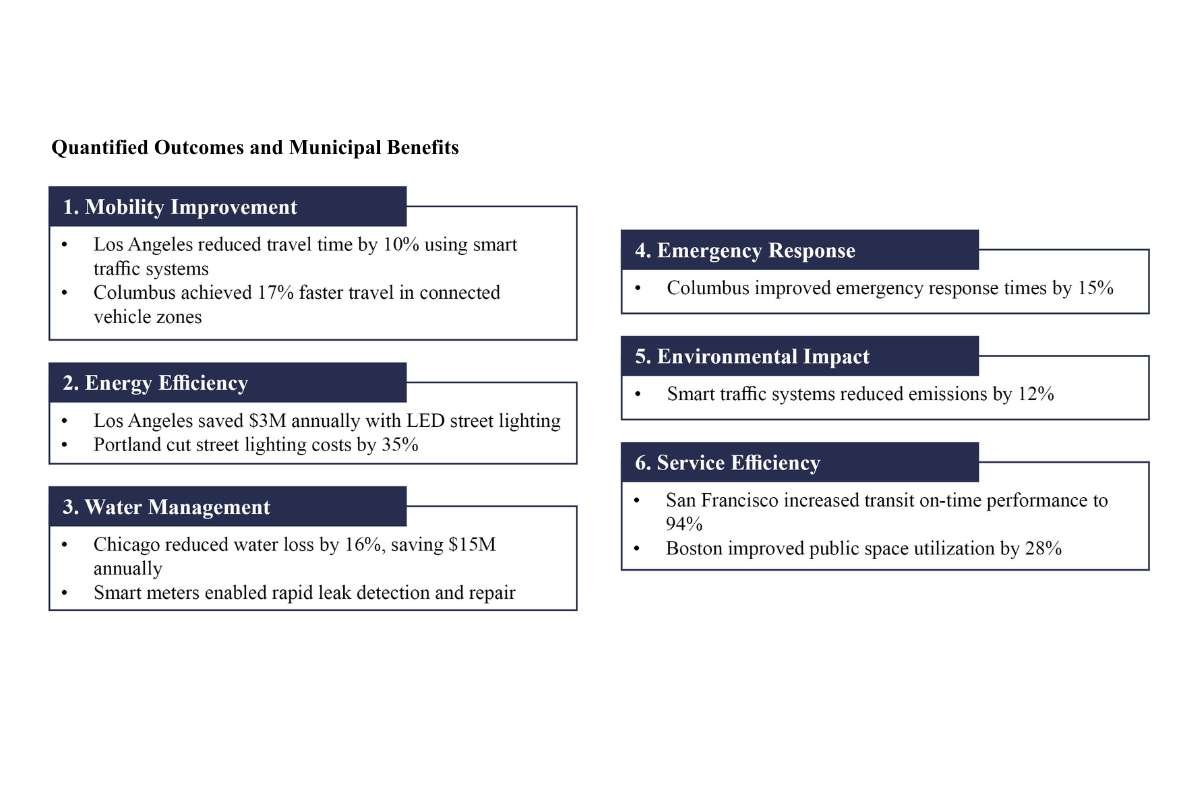
This infographic highlights how cities leveraging IoT infrastructure are achieving measurable gains in efficiency, sustainability, and public service outcomes. It showcases real-world data demonstrating how smart systems translate into tangible financial savings and operational improvements across urban ecosystems.
- Mobility Improvement
- Los Angeles reduced travel time by 10% using smart traffic systems
- Columbus achieved 17% faster travel in connected vehicle zones
- Energy Efficiency
- Los Angeles saved $3M annually with LED street lighting
- Portland cut street lighting costs by 35%
- Water Management
- Chicago reduced water loss by 16%, saving $15M annually
- Smart meters enabled rapid leak detection and repair
- Emergency Response
- Columbus improved emergency response times by 15%
- Environmental Impact
- Smart traffic systems reduced emissions by 12%
- Service Efficiency
- San Francisco increased transit on-time performance to 94%
- Boston improved public space utilization by 28%
Challenges and Future Directions
Smart infrastructure doesn’t arrive without friction. As cities wire themselves with sensors, they also inherit new vulnerabilities, cyber risks, privacy dilemmas, fragmented standards, aging legacy systems, and a shortage of skilled talent to manage it all.
The next leap comes from speed and proximity. With 5G enabling ultra-low latency and edge computing pushing intelligence closer to the source, cities can act in real time. using IoT to build resilient infrastructure has proven transformative where governance is deliberate, boosting efficiency and safety. Cities that align data, AI, and departments aren’t experimenting anymore; they’re setting the blueprint.










