When you start a business, you must choose a business structure that is best for you. This is especially true when you consider the legal and financial aspects of the company. These structures can change how liabilities, limitations, and tax implications apply to a business. In this article, we are going to take a look at two such structures: a sole proprietorship and an S corporation.
So, sole proprietorship vs S Corp, which one is better? But before we put these two head-to-head, we must understand what they exactly are.
What is a Sole Proprietorship?

The meaning of sole proprietorship becomes clear when we decode the two words. ‘Sole’ means ingle, and ‘proprietor’ means owner. Hence, a sole proprietorship means a business that is owned by a single person. This individual is responsible for handling, controlling, and managing all aspects of a business. This means that the person is also a recipient of all the gains and losses that the company incurs. It is suitable for organisations that require personalized attention, for example, a grocery store. There are many features of a sole proprietorship. These features include:
1. Forming and Closing a Business
A sole proprietorship is one of the simplest business structures. Hence, it hardly requires any extensive legal formalities. In some cases, a license or certification might be required to run a business, for example, a drug or alcohol license. The owner can also choose to easily close the business at any time.
2. No Sharing of Profit and Loss
Since the business is run by a single person, he is the only one who is investing in the business and is responsible for all the risks. He will be the sole gainer of profits as well as the sole bearer of losses.
3. Lack of Continuity
In the case of death, imprisonment, or bankruptcy of the owner, the business cannot continue. This happens as there is no one else to take ownership of the business. The only exception is in case there is a beneficiary. Then, a nominee or heir can keep the company running.
These features also make up the advantages and disadvantages of this business structure. You can start or shut down a business without any hassle, as well as deal with the gains and losses. This makes it a very high-risk, high-reward strategy.
Take the fictional case of Soledad Prosepina, who operates a sole proprietorship. The case highlights both the risk and flexibility of a sole proprietorship. It can offer simplicity and control in exchange for unlimited personal liability and limited growth.
What is an S Corp?

An S corp or corporation is a business that can pass its losses, gains, and debts incurred, directly to its shareholders. This is done for federal tax reasons. An S corporation is only available to small businesses with 100 or fewer shareholders. These businesses are often known as ‘pass-through’ entities, as they avoid paying corporate tax, instead making the shareholders responsible for any taxes that are due. Getting an S corporation status requires meticulous attention to issuing shares and crafting detailed shareholding policies. The key features of an S corporation are:
1. Pass-through Taxation
This is the main feature of an S corporation. It makes a company’s taxation efficient by passing it through the shareholders.
2. Single Class of Stock
Any shares or stocks issued under an S corporation are of a single class. Single-class stocks are stocks that are of a single type. This ensures a simple company structure and equal voting rights.
3. Restrictions on Shareholders
There are strict restrictions put on shareholders. For a business or entity, there cannot be more than 100 of them. They must also all be citizens of the U.S or have permanent residency.
Now you have an overview of both these types of structures. But in this debate of sole proprietorship vs S corp, who comes out on top? How do they stack up against each other?
Sole Proprietorship Vs S Corp: Key Differences
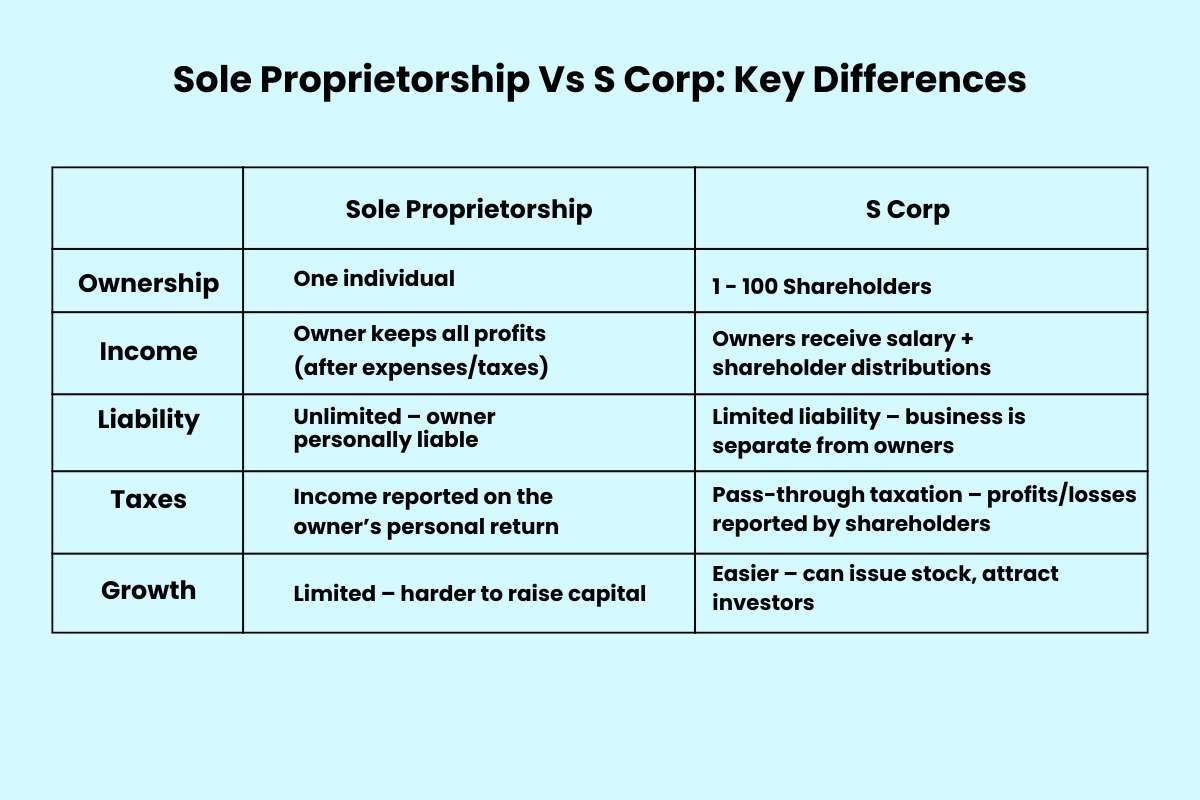
| Sole Proprietorship | S Corp | |
| Ownership | One individual | 1 – 100 Shareholders |
| Income | Owner keeps all profits (after expenses/taxes) | Owners receive salary + shareholder distributions |
| Liability | Unlimited – owner personally liable | Limited liability – business is separate from owners |
| Taxes | Income reported on the owner’s personal return | Pass-through taxation – profits/losses reported by shareholders |
| Growth | Limited – harder to raise capital | Easier – can issue stock, attract investors |
1. Ownership
As mentioned above, one of the key differences between a sole proprietorship vs S corp is how the company is owned. A sole proprietorship is owned by a single person who is responsible for operating nearly everything in the business.
In an S Corp, the shares are divided between different shareholders. Hence, they have multiple people presiding over the enterprise. The majority advantage it allows is bypassing some corporate taxes. There can be anywhere between 1 and 100 shareholders in an S corporation.
2. Income
Businesses that operate under a sole proprietorship model generate income in a smooth and streamlined manner. They offer their services from which the owner generates income. This income covers any expenses, and the owner has to then pay taxes on any profits that are made.
In an S corporation, income is distributed to all the owners. It is done in two different ways, either as dividends or as a salary for an owner acting as an employee. This is known as an owner-employee salary.
3. Liability
Liability protection is the protection that a business owner has against any losses. In a sole proprietorship, as a single owner, you are responsible for any debts and obligations. There is no separation between you and your business. So, if your business has any debt, your personal assets, like your house, car, and personal savings, could be at risk. This means that a sole proprietorship can have unlimited liability.
On the other hand S corporation offers liability protection. This means that business owners are not liable for any debts and losses. It gives business owners a layer of protection by separating them from the business.
4. Taxes
The biggest dividing factor in sole proprietorship vs S Corp is the way each type interacts with taxes. For sole proprietorships, you report your business’s income and expenses on your personal tax return. So, your business income is taxed at your personal income rate.
An S corporation employs a different method to file taxes. It distributes its income amongst its owners in the form of dividends or reasonable salaries. The owners then pay taxes only on these dividends. The choice between sole proprietorship vs S Corp is majorly influenced by this factor.
Thus, opting for an S corporation can substantially reduce employment taxes. Take the example of John, an S Corp owner, who by donating his shares to Fidelity Charitable avoided nearly half a million in capital gain taxes.
5. Growth and Scalability

Sole Proprietorships can be easy to set up and manage, but they can also limit a company’s growth at times. Having unlimited liability can make potential investors hesitant to invest in your business. This can make it harder for you to raise your capital.
An S corporation, on the other hand, can offer a lot of opportunities for scalability. The flexibility in profit allocation can be alluring to investors. Implementing an S corporation can also enhance a business’s creditworthiness. This type of business structure can help smaller businesses gain capital to grow and expand.
These differences between sole proprietorship vs S corp can vastly change the trajectory of your business. It is vital that you plan the structure you want to implement before starting a company. But, how exactly does one go about setting up these structures?
Also Read:
- Sole Proprietorship: A Comprehensive Guide for Aspiring Entrepreneurs
- Running Solo or Tag-Teaming? Sole Proprietorship vs. Partnership Explained
- Business Tax Planning Strategies: Maximizing Tax Efficiency for Your Company
How to Form a Sole Proprietorship?
- Step 1 – Create a Business Name: The name you pick will represent your business. When you start a sole proprietorship, your legal name becomes your business name by default. You can create a separate business name, which is known as a DBA.
- Step 2 – Register Your Business: If you choose to pick a DBA name, then you must register it. Make sure that no other company has the same name as yours. Requirements for a DBA can vary from state to state.
- Step 3 – Apply for an EIN: An EIN is an Employee Identification Number. An EIN identifies your business for tax purposes. You can use your Social Security Number (SSN) to file taxes, but the IRS requires you to have an EIN if you hire any employees.
- Step 4 – Obtain License and Permits: According to the type and sector of your business, you may need certain licenses and permits. For example, if you sell goods, you may need a license that allows you to collect sales tax.
How to Form an S Corp?
- Step 1 – Pick Your Business Type: Forming an S corporation starts by choosing if your company is going to be a Limited Liability Company (LLC) or a C corp. An LLC is a type of business structure that offers liability protection. A C-Corp is owned by multiple shareholders.
- Step 2 – File Paperwork: After selecting your business type, you need to register your business name and domain. You can take the help of a registration agent to help you with the details of any paperwork.
- Step 3 – Get an EIN: Just like in a sole proprietorship, get an Employee Identification Number. It can let you hire employees, file taxes, and open a business account.
- Step 4 – Elect S Corp Status: After the basic steps to start a business have been completed, it is now time to look at S Corp requirements. Make sure that you are a domestic business with no more than 100 shareholders. Also, make sure that all of them have a single class stock. You can file for an S Corp status by filing Form 2553.
Conclusion: Which is Better For You?
This battle of Sole Proprietorship Vs S Corp is one that is full of pros and cons. Which one you choose depends on two main considerations. These are liability and costs. Getting an S Corp status can limit your liability, along with lowering taxes on your profits. However, setting up an S corporation can be extremely complicated. It can also involve heavy upfront costs.
Sole proprietorship, on the other hand, can be easy to start and manage. You also do not have to share your profits. But the unlimited liability can hinder your chances of scalability and growth. It also puts your financial assets at risk.
Ultimately, it depends on a variety of factors. Just keep in mind that whichever you choose is going to decide how you navigate through the sea of taxes and liability.
FAQ
1. Can a sole proprietorship turn into an S corporation?
A sole proprietorship can turn into an S corporation, but not directly. It must first establish itself as an LLC or as a C-Corp.
2. What is an LLC?
LLC stands for Limited Liability Company. It means that its members are not personally liable for any of the company’s debts.
3. What is a C-Corp?
C-Corp is a business structure where the business is legally separate from the owner. So owners or shareholders are taxed separately from the business.