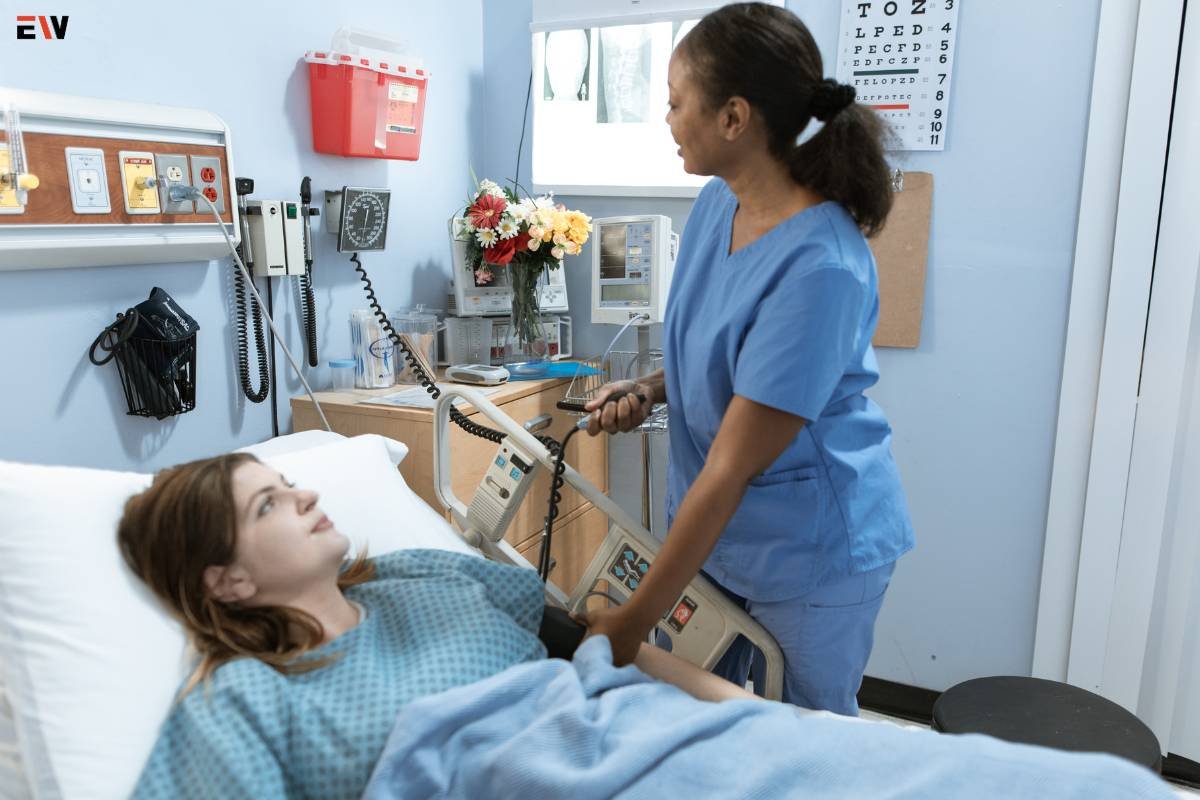
Patient monitoring has undergone a remarkable evolution, revolutionizing healthcare by providing real-time insights into patients’ physiological parameters and overall well-being. This comprehensive exploration delves into the significance, technological advancements, applications, challenges, and future trends of patient monitoring.
The Significance of Patient Monitoring
1. Early Detection of Health Issues
Monitoring enables healthcare professionals to detect health issues at an early stage. Continuous tracking of vital signs and other relevant parameters allows for timely intervention, preventing the escalation of health problems and improving patient outcomes.
2. Customized Treatment Plans
Tailoring treatment plans to individual patient needs is facilitated by monitoring. By gathering real-time data, healthcare providers can adjust medications, therapies, and interventions based on the specific requirements of each patient, optimizing the effectiveness of treatments.
3. Remote Patient Management
Advances in monitoring technology have led to the development of remote monitoring solutions. Patients can now be monitored from the comfort of their homes, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and enabling healthcare professionals to manage chronic conditions more effectively.
4. Improved Patient Safety
Monitoring enhances safety by alerting healthcare teams to potential complications or adverse events. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of medical errors, improves response times, and contributes to a safer healthcare environment for patients.
5. Enhanced Clinical Decision-Making
Real-time data provided by monitoring systems empowers healthcare professionals to make informed and timely clinical decisions. This data-driven approach enhances diagnostic accuracy, facilitates treatment planning, and improves overall decision-making in patient care.
Technological Advancements
1. Wearable Devices
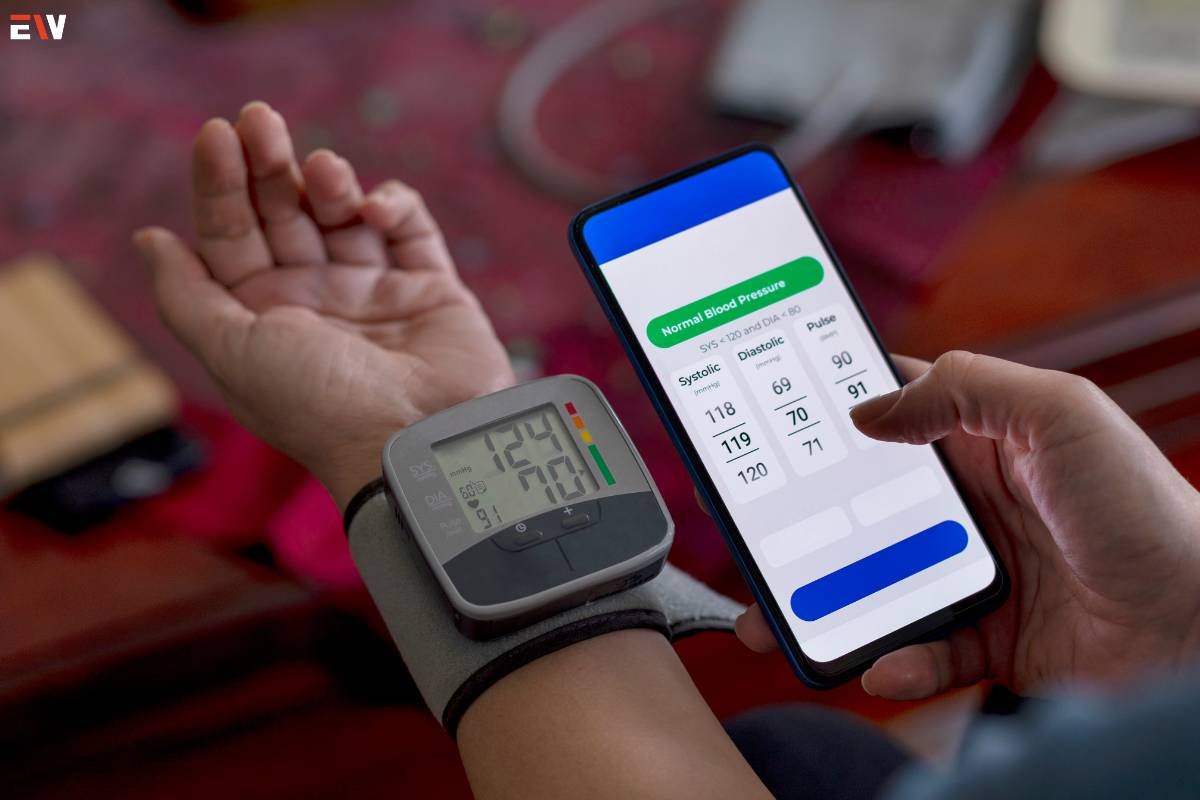

Wearable devices have become a cornerstone of patient monitoring. Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and other wearables allow individuals to track their health metrics continuously, providing valuable data for both patients and healthcare providers.
2. Internet of Things (IoT)
The integration of IoT in healthcare has transformed patient monitoring. Connected devices and sensors gather and transmit data seamlessly, creating a network of information that enhances the monitoring and management of patients’ health conditions.
3. Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
Telemedicine platforms leverage monitoring for remote healthcare delivery. Patients can participate in virtual consultations, and healthcare providers can monitor vital signs and other parameters remotely, fostering more accessible and patient-centric care.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of patient data, providing insights into patterns, trends, and potential risks. These technologies contribute to predictive analytics, helping healthcare professionals anticipate and prevent adverse events.
5. Smart Implants and Biosensors
Smart implants and biosensors are revolutionizing monitoring for individuals with chronic conditions. These devices can be implanted to monitor specific health parameters continuously, providing valuable data for managing conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
Applications of Patient Monitoring
1. Critical Care Monitoring
In intensive care units (ICUs), patient monitoring is crucial for tracking vital signs, oxygen levels, and other parameters in critically ill patients. Continuous monitoring allows for rapid responses to changes in patients’ conditions, improving outcomes in critical care settings.
2. Chronic Disease Management
Patients with chronic conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases, benefit from continuous monitoring. This approach assists in managing these conditions more effectively, preventing complications, and empowering patients to actively participate in their care.
3. Postoperative Monitoring
Monitoring is essential in the postoperative phase, ensuring that patients recover safely from surgical procedures. Continuous tracking of vital signs and other parameters helps identify any postoperative complications early on, enabling timely interventions.
4. Maternal and Fetal Monitoring
In obstetrics, patient monitoring plays a crucial role in ensuring the well-being of both mothers and infants. Continuous monitoring during pregnancy and childbirth allows healthcare professionals to detect and address potential complications, contributing to safer deliveries.
5. Cardiac Monitoring
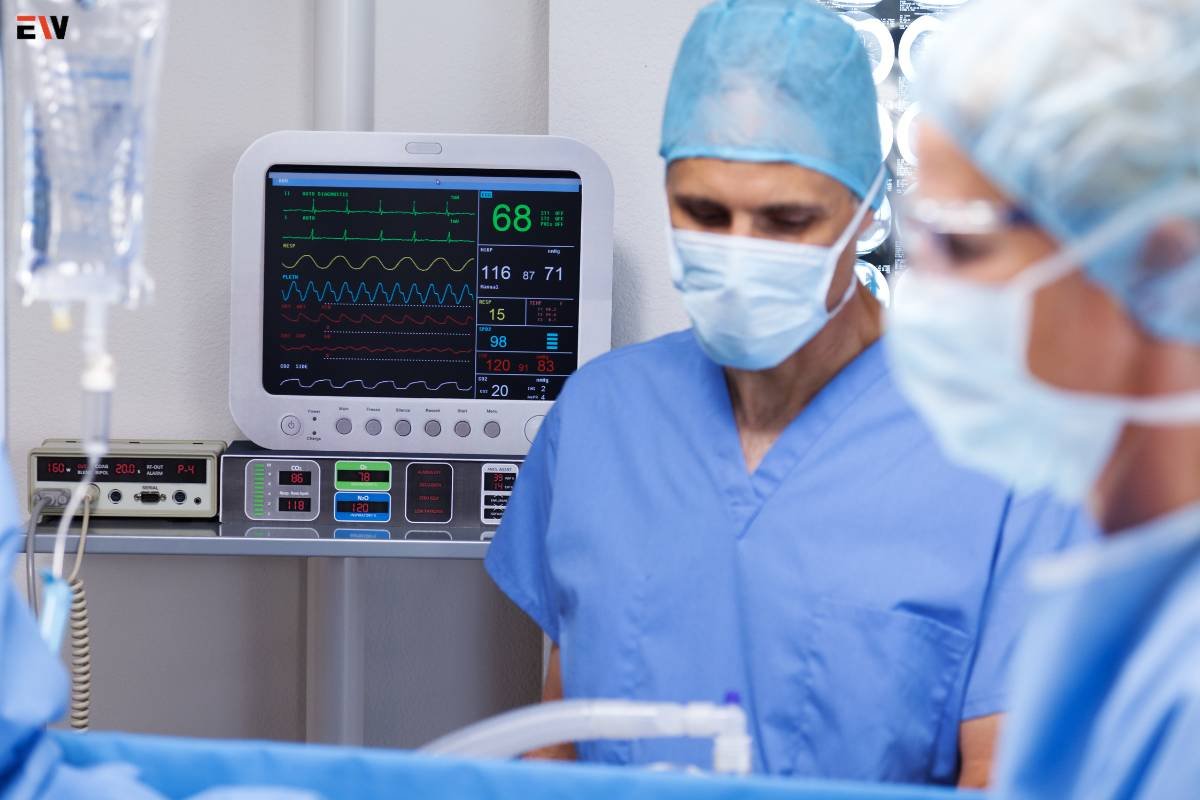
Patients with heart conditions benefit from advanced cardiac monitoring solutions. Continuous electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring, Holter monitoring, and implantable cardiac devices help manage and monitor heart rhythms, providing valuable data for cardiac care.
Challenges in Monitoring
1 .Data Security and Privacy Concerns
The digitization of patient data raises concerns about data security and privacy. Safeguarding sensitive health information is crucial to ensure patient trust and compliance with data protection regulations.
2. Interoperability Issues
The integration of diverse patient monitoring systems can be challenging due to interoperability issues. Standardization efforts are ongoing to facilitate seamless data exchange between different devices and healthcare platforms.
3. Overwhelming Data Volume
The abundance of data generated by monitoring systems can be overwhelming for healthcare professionals. Effectively managing and interpreting large volumes of data require advanced analytics tools and strategies.
4. Resource Constraints
Implementing comprehensive patient monitoring systems may face resource constraints, particularly in healthcare settings with limited budgets. The cost of acquiring, maintaining, and upgrading monitoring technologies can be a barrier to widespread adoption.
5. User Training and Adoption
Ensuring that healthcare professionals and patients are adequately trained to use monitoring devices is essential. Resistance to change and insufficient training can hinder the successful adoption of monitoring technologies.
6. Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to regulatory standards and certifications is a challenge in the rapidly evolving landscape of patient monitoring. Ensuring that devices meet safety and performance requirements is critical for regulatory compliance.
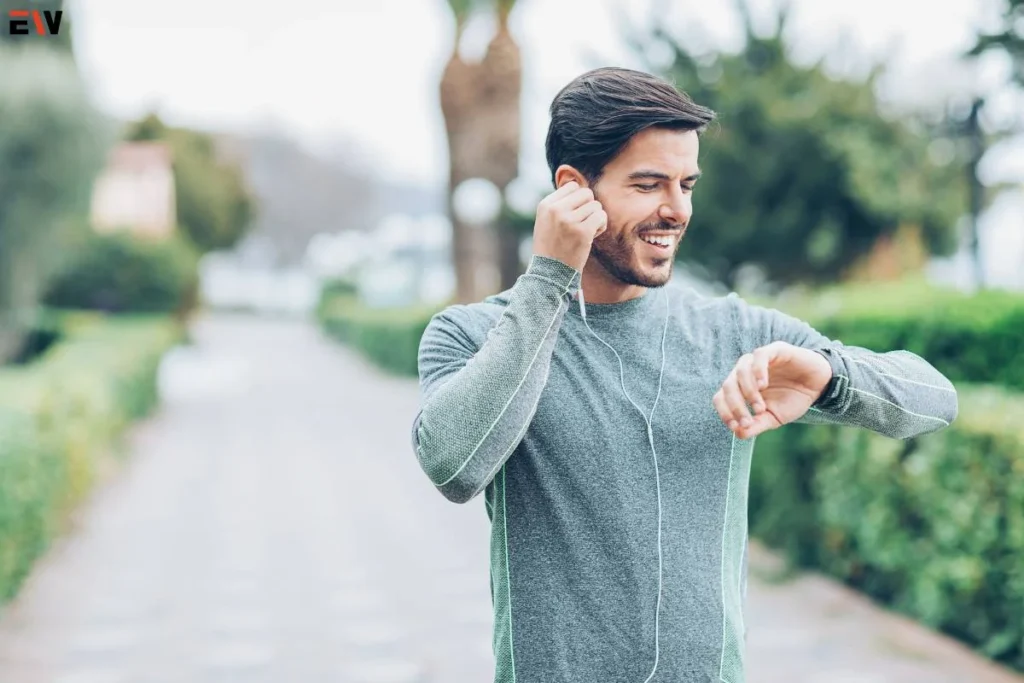

The Rise of Wearable Health Tech: Transforming Personal Wellness
In an era where technology continues to infiltrate every aspect of our lives, the realm of personal wellness is no exception. Wearable health tech has emerged as a revolutionary force in the pursuit of improved health and well-being.
Future Trends
1. Integration of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
The incorporation of AR and VR in patient monitoring may enhance the visualization of patient data. Healthcare professionals can use immersive technologies for real-time data analysis and training purposes.
2. Advancements in Remote Monitoring Solutions
Remote monitoring will continue to evolve with advancements in technology. Continuous improvements in connectivity, wearables, and telemedicine platforms will further enhance the capabilities of remote monitoring.
3. Blockchain for Data Security
Blockchain technology holds promise for addressing data security concerns in monitoring. Its decentralized and secure nature can provide a robust framework for managing and securing patient data.
4. Personalized and Predictive Medicine
Monitoring will increasingly contribute to personalized and predictive medicine. Advanced analytics and AI algorithms will enable healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans based on individual patient data, optimizing outcomes.
5. Home-based Monitoring for Aging Populations
As populations age, there will be a growing emphasis on home-based monitoring solutions. Monitoring technologies will support aging individuals in managing chronic conditions and maintaining their independence.
6. Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
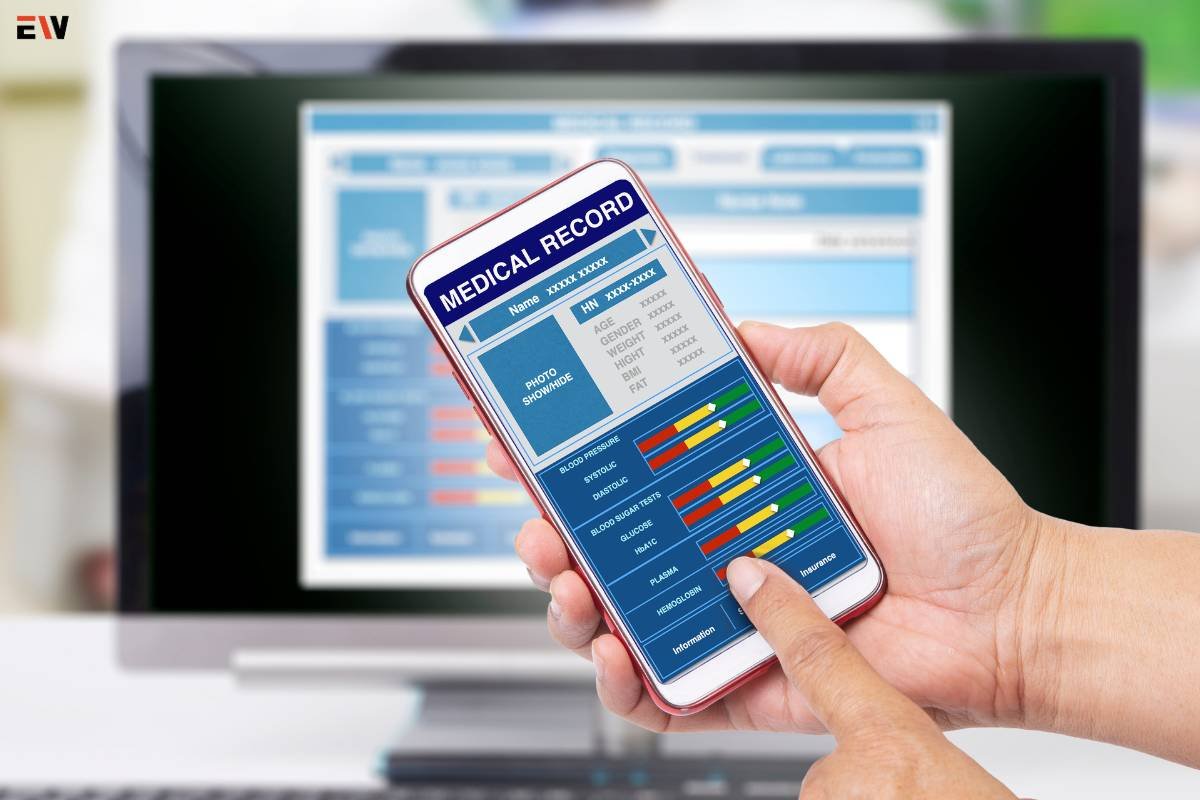

Seamless integration with EHRs will enhance the continuity of care. Patient monitoring data can be directly incorporated into electronic health records, providing a comprehensive and centralized view of patients’ health histories.
7. Expansion of Remote Monitoring in Chronic Care
Remote monitoring will expand its reach in managing chronic conditions. Patients with conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and respiratory diseases will benefit from continuous monitoring and virtual healthcare interactions.
8. Enhanced Data Analytics for Clinical Decision Support
Advances in data analytics will provide healthcare professionals with more sophisticated clinical decision support tools. Real-time analysis of monitoring data will facilitate more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment recommendations.
Conclusion
Patient monitoring has transformed healthcare delivery, providing a continuous stream of valuable data for informed decision-making and improved patient outcomes. From wearable devices to advanced sensors and remote monitoring solutions, the evolution of monitoring continues to shape the future of healthcare.










