Source- TWI Global
In the realm of advanced technology, digital twin technology has emerged as a ground-breaking innovation with profound implications across various industries. Offering a virtual representation of physical assets, processes, and systems, digital twin technology enables real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization, leading to improved performance, efficiency, and decision-making capabilities.
Understanding Digital Twin Technology
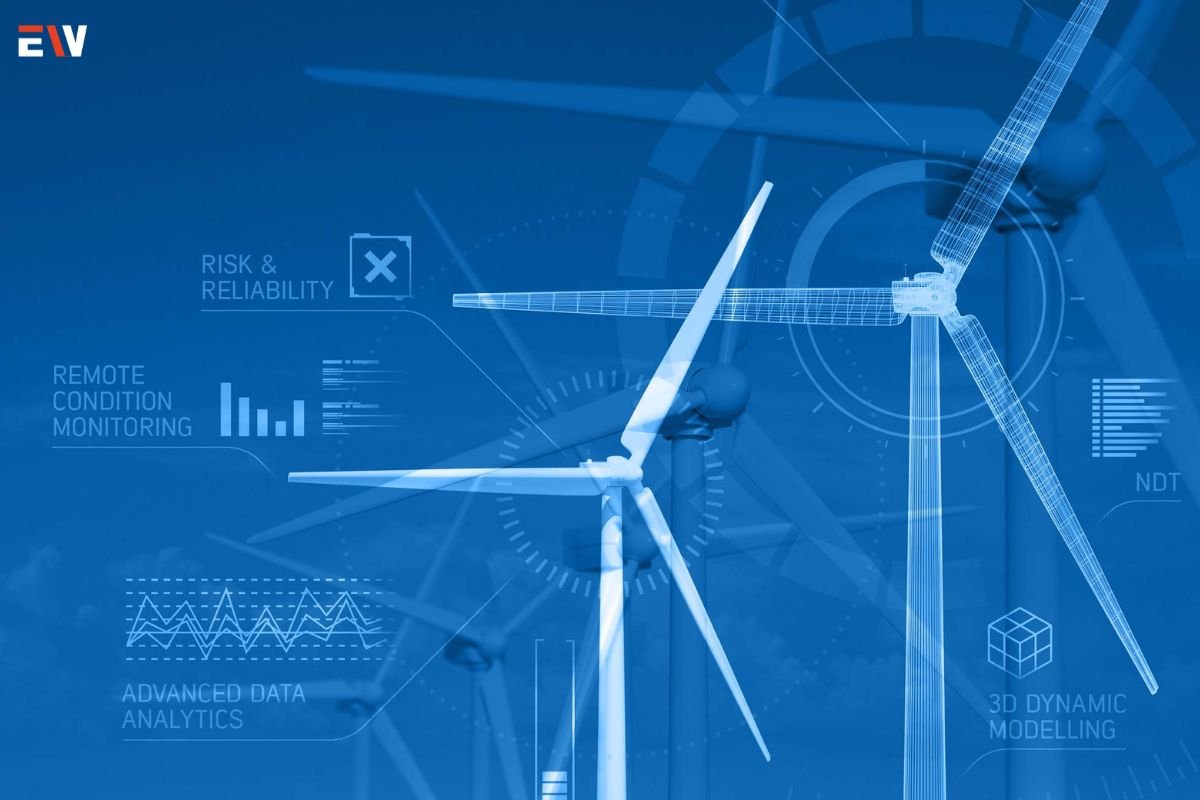
The twin technology involves creating a digital replica or simulation of physical objects, systems, or processes, using real-time data and sensor information to mimic their behavior and characteristics. These virtual models enable organizations to monitor, analyze, and simulate the performance of their assets and operations, providing valuable insights and predictive capabilities for decision-making and optimization. Digital twins can range from simple models of individual components to complex simulations of entire ecosystems, such as buildings, factories, cities, or even entire supply chains.
Applications of Digital Twin Technology
The twin technology finds applications across a wide range of industries and sectors, including:
1. Manufacturing
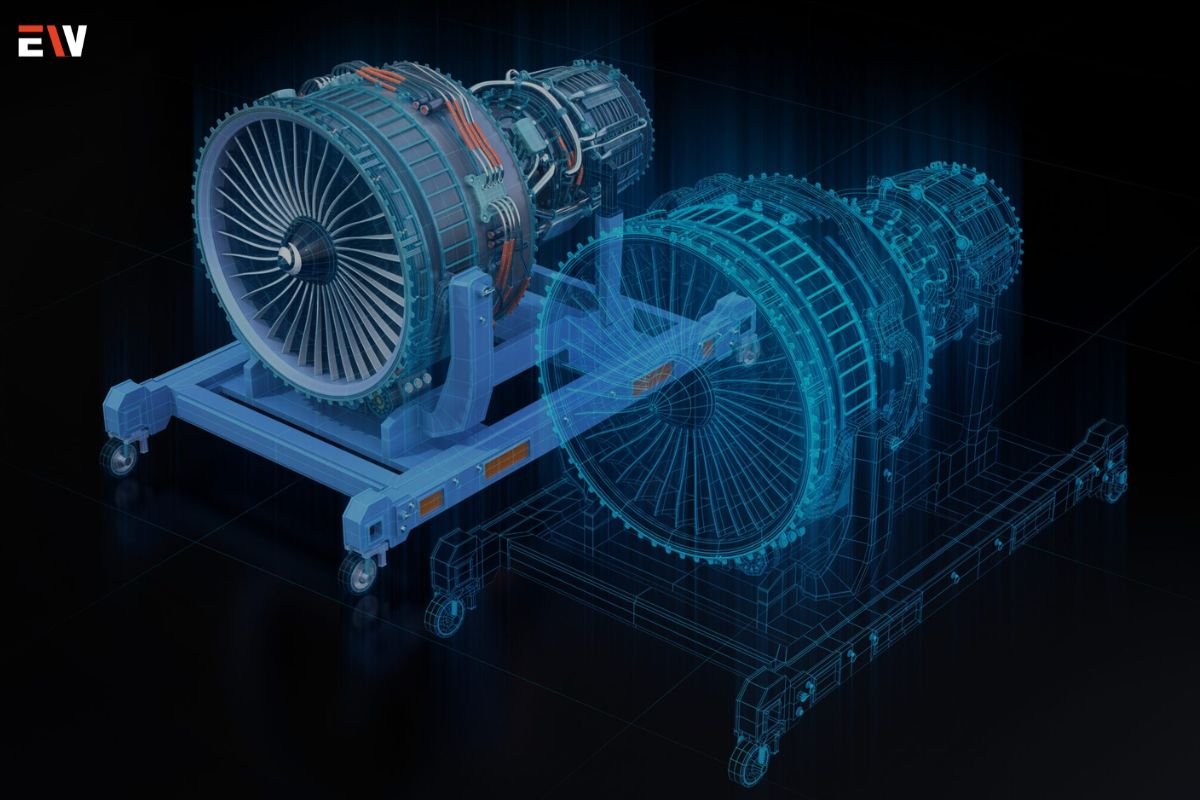
In manufacturing industries, digital twins are used to simulate production processes, optimize equipment performance, and predict maintenance needs. By creating virtual replicas of manufacturing facilities and equipment, organizations can identify inefficiencies, reduce downtime, and improve overall productivity.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, digital twins are employed to create personalized patient models, simulate medical procedures, and optimize treatment plans. Digital twins of organs, tissues, or entire human bodies enable doctors to visualize and analyze patient data in real-time, leading to more accurate diagnoses and improved patient outcomes.
3. Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace and defense sectors, digital twins are used to simulate aircraft, spacecraft, and weapon systems, allowing engineers to test performance, predict failures, and optimize designs before physical prototypes are built. Digital twins also enable predictive maintenance and condition monitoring for critical assets, ensuring mission readiness and operational efficiency.
4. Smart Cities
In urban planning and development, digital twins are employed to create virtual models of cities, infrastructure, and public services. By integrating data from various sources, such as sensors, IoT devices, and social media, digital twins enable city planners to optimize traffic flow, manage energy consumption, and enhance public safety and security.
5. Energy and Utilities
In the energy and utilities sector, digital twins are used to monitor and optimize the performance of power plants, grids, and distribution networks. By creating virtual replicas of energy assets and systems, organizations can identify inefficiencies, optimize resource allocation, and improve reliability and resilience.
Benefits of Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology offers a wide range of benefits for organizations, including:
1. Predictive Insights
Digital twins enable organizations to predict and prevent potential issues before they occur by simulating scenarios, analyzing data trends, and identifying anomalies in real time.
2. Optimized Performance
By monitoring and analyzing the behavior of physical assets and processes, organizations can identify opportunities for optimization, improve efficiency, and maximize productivity.
3. Cost Savings

Digital twins help reduce operational costs by minimizing downtime, optimizing resource allocation, and avoiding costly repairs or maintenance activities through predictive maintenance strategies.
4. Informed Decision-Making
Digital twins provide valuable insights and actionable intelligence that empower organizations to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities for innovation and growth.
5. Enhanced Collaboration
Digital twins facilitate collaboration and communication among cross-functional teams by providing a common platform for data sharing, visualization, and analysis, leading to improved coordination and alignment across the organization.
Future Prospects of Digital Twin Technology
As digital twin technology continues to evolve and mature, its future prospects are promising, with potential advancements in areas such as:
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration
Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms into digital twin platforms will enhance predictive capabilities, enabling organizations to anticipate and adapt to dynamic operating conditions more effectively.
2. Edge Computing and IoT Integration
Integration of edge computing and Internet of Things (IoT) devices into digital twin ecosystems will enable real-time data processing and analysis at the network edge, improving responsiveness and reducing latency for mission-critical applications.
3. Blockchain for Data Security
Integration of blockchain technology into digital twin platforms will enhance data security and integrity, providing tamper-proof audit trails and ensuring trust and transparency in data exchange and transactions.
4. 3D Visualization and Immersive Technologies

The adoption of 3D visualization and immersive technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), will enhance the user experience and enable immersive, interactive simulations for training, design, and decision support.
5. Digital Twin Ecosystems and Interoperability
The development of open-source digital twin frameworks and interoperability standards will foster collaboration and innovation across industries, enabling seamless integration and interoperability between different digital twin platforms and ecosystems.
Conclusion
Digital twin technology represents a transformative paradigm shift in the way organizations design, operate, and optimize their assets and processes. By creating virtual replicas of physical objects, systems, and environments, digital twins enable real-time monitoring, analysis, and simulation, leading to improved performance, efficiency, and decision-making capabilities.










