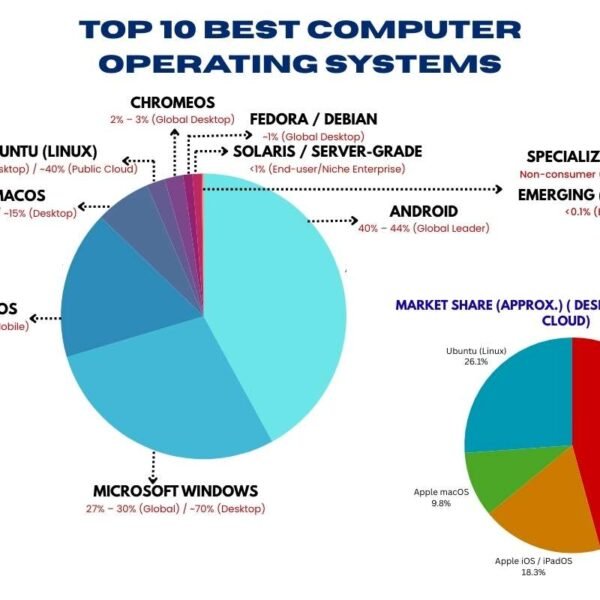
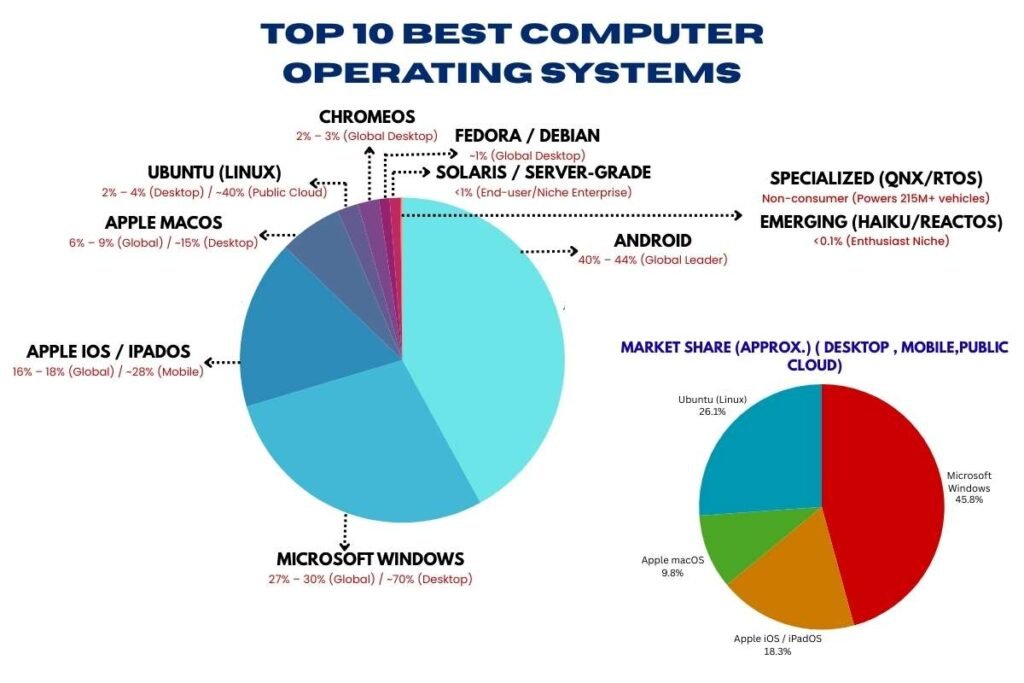
Employee self-evaluations are a crucial component of performance management systems in organizations. They provide employees with the opportunity to reflect on their performance, set goals, and engage in a meaningful dialogue with their supervisors. This process not only promotes self-awareness and personal development but also enhances communication and transparency within the organization. This article explores the importance of employee self-evaluations, best practices for implementation, and how they can be effectively integrated into performance management systems.
Importance of Employee Self-Evaluations
1. Promotes Self-Reflection
Self-evaluations encourage employees to take a step back and assess their own performance objectively. This process of self-reflection helps individuals identify their strengths and areas for improvement, fostering a culture of continuous learning and development.
2. Enhances Communication
Self-evaluations open up a two-way communication channel between employees and their supervisors. By sharing their own perspectives on their performance, employees can provide valuable insights that might otherwise be overlooked. This dialogue promotes mutual understanding and alignment of expectations.
3. Empower Employees

Allowing employees to evaluate their own performance gives them a sense of ownership and responsibility. This empowerment can lead to increased motivation and engagement, as employees feel more involved in their own development and career progression.
4. Informs Performance Reviews
Self-evaluations provide a balanced view of an employee’s performance when combined with supervisor evaluations. This comprehensive perspective ensures that performance reviews are fair, objective, and based on a holistic understanding of an employee’s contributions.
5. Identifies Training and Development Needs
By highlighting their own strengths and weaknesses, employees can help identify specific areas where they need additional training or support. This information is invaluable for HR and management in designing targeted development programs that address individual and organizational needs.
Best Practices for Implementing Employee Self-Evaluations
1. Clear Guidelines and Criteria
Provide employees with clear guidelines and criteria for completing their self-evaluations. This includes outlining the specific areas of performance to be assessed, such as job responsibilities, goal achievement, skills, and competencies. Clear instructions help ensure consistency and accuracy in the evaluations.
2. Structured Format
Use a structured format for self-evaluations to standardize the process and make it easier for employees to complete. This can include rating scales, open-ended questions, and prompts to guide their reflections. A structured format also simplifies the review process for supervisors.
3. Encourage Honesty and Objectivity
Encourage employees to be honest and objective in their self-assessments. Emphasize that self-evaluations are not about self-promotion or criticism, but rather an opportunity for genuine self-reflection and growth. Creating a supportive environment where employees feel comfortable being candid is crucial.
4. Link to Performance Goals
Align self-evaluations with individual and organizational performance goals. This ensures that employees are reflecting on their contributions in the context of the broader objectives of the organization. Linking self-evaluations to goals also helps in setting realistic and relevant development plans.
5. Provide Training and Support

Offer training and support to employees on how to conduct effective self-evaluations. This can include workshops, tutorials, and examples of well-completed evaluations. Providing support helps employees understand the purpose of self-evaluations and how to approach them thoughtfully.
6. Integrate into the Performance Management System
Integrate self-evaluations into the overall performance management system. This includes incorporating them into regular performance review cycles and using the insights gained to inform development plans, promotions, and other HR decisions. Integration ensures that self-evaluations are taken seriously and have a tangible impact.
Effective Self-Evaluation Questions and Prompts
1. Job Responsibilities
- How well do you feel you have performed your key job responsibilities over the past review period?
- Can you provide specific examples of accomplishments or successes in your role?
2. Goal Achievement
- Have you met the goals set for you during the last review period? If not, what were the obstacles?
- What new goals would you like to set for the upcoming period, and what steps will you take to achieve them?
3. Skills and Competencies
- Which skills and competencies do you feel are your strongest, and how have they contributed to your performance?
- Are there any skills or areas where you feel you need improvement or additional training?
4. Collaboration and Teamwork
- How would you describe your ability to work with colleagues and contribute to team projects?
- Can you provide examples of successful collaboration or instances where teamwork could have been improved?
5. Professional Development
- What professional development activities have you engaged in during the review period (e.g., training, certifications, conferences)?
- What additional development opportunities would you like to pursue, and how do you think they will benefit your role and the organization?
6. Feedback and Improvement
- How have you responded to feedback received from supervisors, colleagues, or clients?
- What actions have you taken to address areas of improvement identified in previous reviews?
Integrating Self-Evaluations into Performance Management
1. Pre-Review Preparation
Before performance reviews, employees should complete their self-evaluations and submit them to their supervisors. This allows supervisors to review the self-assessments and prepare for the discussion, ensuring a more informed and productive review meeting.
2. Collaborative Review Meetings
During performance review meetings, use the self-evaluation as a starting point for discussion. This collaborative approach ensures that both the employee’s and supervisor’s perspectives are considered, leading to a more balanced and constructive conversation.
3. Actionable Development Plans

Based on the insights gained from self-evaluations and review meetings, create actionable development plans. These plans should outline specific goals, development activities, and timelines, providing a clear roadmap for the employee’s growth and progress.
4. Continuous Feedback
Encourage continuous feedback and regular check-ins between formal review periods. This ongoing communication helps address issues in real time, reinforce positive behaviors, and keep development plans on track.
5. Monitor and Evaluate
Monitor the effectiveness of the self-evaluation process and make adjustments as needed. Gather feedback from employees and supervisors to identify areas for improvement and ensure that the process remains relevant and valuable.
Conclusion
Employee self-evaluations are a powerful tool for enhancing performance management and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. By promoting self-reflection, enhancing communication, and empowering employees, self-evaluations contribute to individual and organizational success.
Implementing best practices and integrating employee self-evaluations into the performance management system ensures that they are effective and meaningful. As organizations continue to evolve, leveraging self-evaluations will be essential in building a motivated, engaged, and high-performing workforce.