Steve Jobs, Jeff Bezos, and other top innovators didn’t just tell their teams what to do. Instead, they understood the power of democratic leadership. The traditional command-and-control model simply can’t keep up with the modern workplace. And that is why you need a way to harness the collective intelligence and commitment of your entire team.
That’s where democratic leadership, or participative leadership, comes in. It’s a style where leaders involve team members in the decision-making process. This approach promotes creativity and ownership. It is also the essential ingredient for building a resilient, high-performing team in the modern business.
So, what is it and how can you apply it? Let’s get into it together.
What is democratic leadership? Definition, characteristics, and types
As John Gastil, in his 1994 article, “A Definition and Illustration of Democratic Leadership” for the Human Relations journal, said, “Distributing responsibility among the membership, empowering group members, and aiding the group’s decision-making process.”
This quote perfectly encapsulates what it means to be a democratic leader in your organization.
In “Leadership and Group Life Lewin and his colleagues, Ronald Lippitt and Ralph K. White, spoke about the three primary leadership styles. These styles were democratic, laissez-faire, and autocratic. They conducted a number of interviews with business leaders and employees and concluded that the democratic style was the most popular of the three.
As the name suggests, the democratic or participative leadership style is one where leaders actively seek input and feedback from team members. The team plays an important role in making decisions. In this style, leaders encourage participation, open communication, and shared responsibility across the organization.
Characteristics of Democratic Leadership and how to identify it?
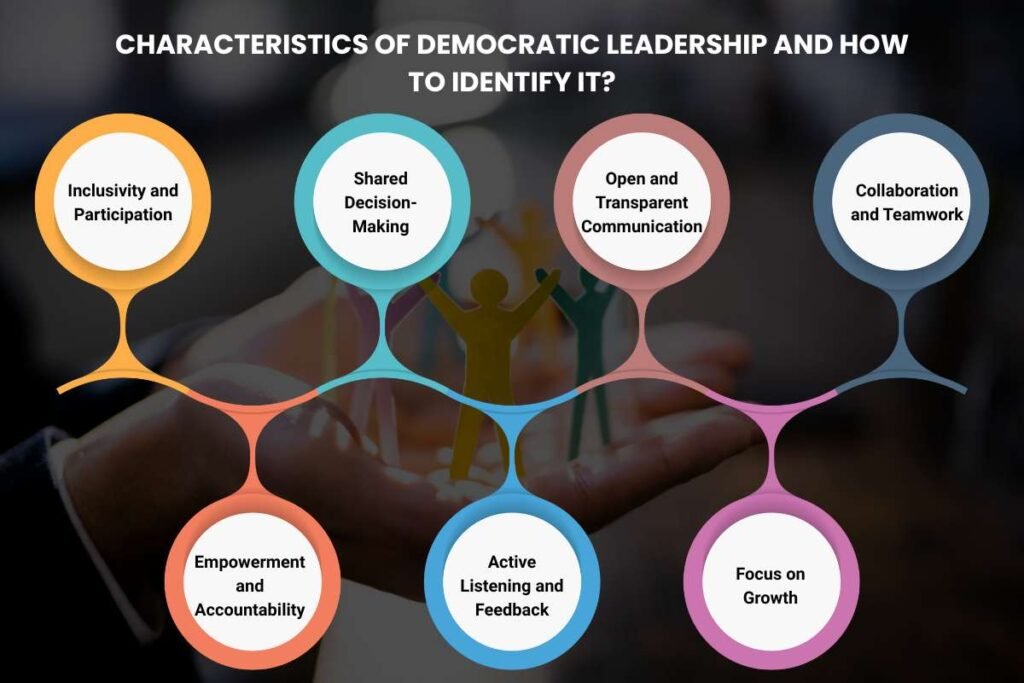
Participative leadership revolves around the idea of involving your team. In this style, the leader acts more as an implementer than a strict commander.
But what are the other characteristics of this style? Here’s what is at the core of being a democratic leader:
- Inclusivity and Participation: Democratic leaders actively encourage all team members to contribute. Their contribution comes in the form of ideas, opinions, and suggestions. The leader believes in the value of diverse perspectives.
- Shared Decision-Making: Input from the team is sought and considered seriously before a final decision is made. The process is collaborative at its core. Though the leader typically retains the final authority and accountability for the outcome.
- Open and Transparent Communication: Information is shared openly with the team. The leader ensures members are well-informed and can provide meaningful input. This fosters trust and a clear understanding of goals and issues.
- Collaboration and Teamwork: The environment strongly promotes working together. The leader facilitates brainstorming sessions and discussions. The team members are encouraged to help each other arrive at creative solutions.
- Empowerment and Accountability: Employees have a degree of autonomy and ownership. But this autonomy comes with shared responsibility and accountability for team results.
- Active Listening and Feedback: Leaders excel at active listening, giving sincere consideration to team members’ concerns and feedback. They are open-minded and willing to adapt plans based on input.
- Focus on Growth: This style often encourages employee development by involving them in higher-level strategic and problem-solving activities.
3 Types of Democratic Leadership: Find out which one suits your Organization

There are three types of participative leadership. Here’s what they are and how they differ:
Type 1: Consultative leadership style
This is the most common form, where the leader acts like a consultant to the team. In this type, the leader plays a central role. They actively ask for input, ideas, and suggestions from team members. The leader makes the final decision alone after carefully considering all the feedback. The team’s role is advisory, which is why it is called consultative.
It is best for decisions where the leader has specialized knowledge, but employee buy-in is still essential for implementation.
Type 2: Collaborative leadership style
You can also call it the true democratic leadership style. This style is closer to the true definition of “democracy” in that the leader is more of a facilitator of a group decision. The leader gathers input and facilitates discussion. They encourage a vote or majority rule among the team. The decisions in this style are taken by the vote of the majority. The leader has one vote or acts as the tie-breaker. The responsibility for the decision is shared between the leader and the team.
It is perfect for solving complex problems where diverse expertise is needed. It is implemented when time allows for extensive discussion.
Type 3: Consensus-driven leadership style
This requires the highest level of participation by the team. In this type, the goal is to come to a complete agreement. The leader facilitates the discussion between the team. They guide the team toward a solution that everyone can agree upon. The team must reach a unanimous or near-unanimous agreement before any action is taken. The leader essentially has a veto or a single voice.
Implement this type when you have critical decisions requiring absolute commitment and buy-in from all stakeholders.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Democratic Leadership?
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Employees feel valued, leading to loyalty, productivity, and reduced turnover. | Collecting input from everyone can delay outcomes, reducing agility. |
| Open discussions foster diverse ideas and problem-solving. | Consultative style can hinder rapid response when quick decisions are needed. |
| Participation builds trust, respect, and shared purpose. | Input from less knowledgeable members may dilute decision quality. |
| Multiple perspectives create well-rounded, thoughtful solutions. | Ignored ideas may lead to resentment or disengagement. |
| Transparency and inclusivity enhance morale and strengthen trust. | Without clear communication and defined roles, confusion and inefficiency arise. |
How to implement democratic leadership in your workplace?
Now that you know almost everything about this style of leadership, you might be planning on implementing it, but how?
Let’s take a look at a step-by-step process of implementing participative leadership in your organization, shall we?
Step 1: Establish Clear Boundaries and Expectations

Before inviting participation, the leader must define the scope of the team’s power. You must state which decisions the team will vote on (Collaborative), which they will advise on (Consultative), and which the leader must make alone (e.g., budget, compliance).
Step 2: Prepare and Empower the Team
Democratic leadership works best with a skilled, engaged team. For that, you must share all relevant data, constraints, and context before asking for input. Remember, a well-informed team makes better decisions. Assign clear roles for research, data gathering, or presenting options to encourage a sense of ownership over the input process.
Step 3: Solicit and Facilitate Input
This is the core democratic phase, where the leader acts as a fair, impartial facilitator. The leader must genuinely listen, summarize arguments, and ensure all viewpoints are accurately understood before moving forward. Your role is to keep the discussion focused on the objectives, challenge assumptions, and mediate disagreements. Do not push your own preferred solution.
Step 4: Decide and Justify
Once input is gathered, the decision must be formalized and explained. Now, this can be different based on the style of democratic leadership you implement. You might either make the final choice or facilitate the group vote/agreement. Remember to record the final decision and the steps taken to arrive at it for transparency and accountability.
Step 5: Implement, Review, and Give Feedback
The process doesn’t end with the decision; it requires follow-through. Regularly check progress and encourage the team to review the effectiveness of the decision made. After the project or decision is complete, hold a brief session to discuss the democratic process itself. Ask your team questions like what worked? What could be improved next time? This refines the team’s ability to operate democratically.
Hear about the 4 leaders who proved Democratic Leadership wins?
Here are some of the famous leaders who implemented this style of leadership in their workplaces:

- Sundar Pichai (CEO, Google/Alphabet): He is known for his inclusive and approachable leadership style. Pichai encourages open communication, team input, and consensus-building. This style has helped Google maintain innovation while managing large, diverse teams.
- Bill Gates (Co-founder, Microsoft): Gates was known for involving his teams in brainstorming sessions and encouraging debate. This tradition of Bill Gates has helped Microsoft grow through collective innovation.
- Abraham Lincoln (16th U.S. President): Lincoln famously formed a “team of rivals” in his cabinet. He encouraged diverse viewpoints and debates to shape policies, particularly during the Civil War.
- Herb Kelleher (Co-founder & CEO, Southwest Airlines): He nurtured a culture where employees’ input was highly valued in operational and customer service strategies. This made Southwest famous for being an employee-friendly airline.
What sets the democratic leadership style apart from other styles?
| Leadership Style | Difference from Democratic Leadership |
|---|---|
| Autocratic | Democratic leaders share decision-making power with the team, while Autocratic leaders make all decisions independently. |
| Laissez-Faire | Democratic leaders guide discussions and make the final call, while Laissez-faire leaders are completely hands-off, letting the team decide and operate with minimal direction. |
| Transformational | Democratic leaders are focused on shared decision-making, while Transformational leadership is focused on inspiring and motivating followers toward a shared vision. |
| Transactional | Democratic leaders rely on team input and collaboration, while Transactional leadership relies on a “rewards and punishments” system to motivate performance. |
| Servant | Democratic leaders prioritize group decision-making, while Servant leadership prioritizes the well-being and growth of individual team members. |
| Bureaucratic | Democratic leaders encourage flexibility and new ideas from the team, while Bureaucratic leadership demands strict adherence to rules and procedures. |
Conclusion:
Democratic leadership is no longer just a soft skill you should know about. Now, it is a necessity for modern, high-performing teams. By embracing it, organizations successfully tap into the full intelligence, creativity, and commitment of their workforce. This participative approach promotes an environment of trust, boosts morale, and ensures that solutions are well-rounded and supported by the very people who will implement them.
While it demands more time and better communication, the payoff is a resilient culture where employees feel empowered and accountable. In an era defined by complex problems, sharing the power of decision-making is the most effective path to sustainable innovation and success.
FAQs
1. What are the key ethical challenges a democratic leader might face?
The main ethical challenge is managing the “tyranny of the majority,” where a popular decision might marginalize or harm a minority group. A democratic leader must also ethically balance the desire for consensus with the need to protect confidential or sensitive information. Transparency is important, but it must be tempered by responsibility.
2. When is the democratic leadership style least effective or appropriate?
This style is generally least effective during times of crisis or high-pressure situations that require immediate action. It is also a poor fit when leading a team of inexperienced or low-skilled employees. Quick, urgent decisions are better handled by an authoritative approach.
3. How does participative leadership influence an organization’s innovation rate?
Participative leadership increases the rate of innovation because it actively encourages diverse perspectives and creative problem-solving from all team levels. By creating a safe environment, the leader makes employees comfortable with sharing and experimenting with new, unconventional ideas. This diversity of thought leads to more robust and unique solutions.
4. What steps can a leader take to transition from an autocratic to a democratic style?
The first step is gradual implementation, starting with low-stakes decisions to build team confidence and trust. The leader must also immediately increase transparency about information and rationale. Finally, they should coach team members on how to effectively contribute and hold them accountable for the quality of their input.










