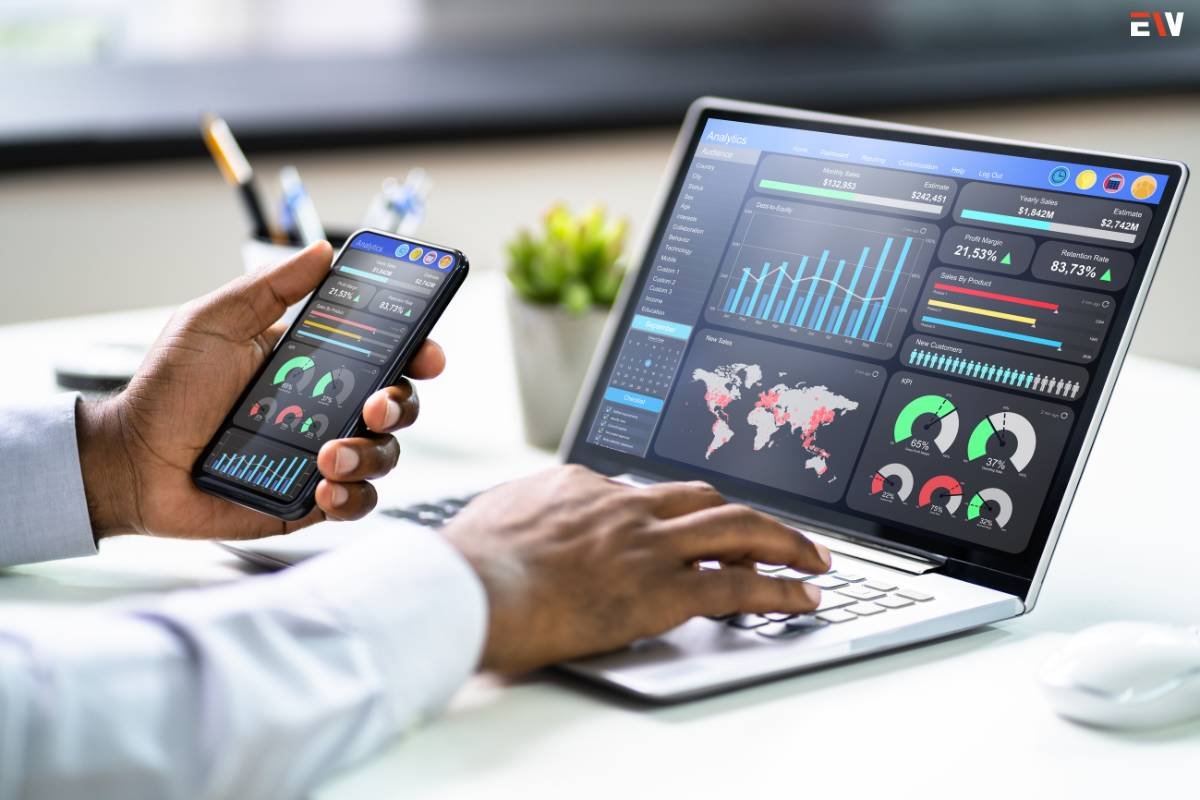
In today’s digital economy, businesses thrive on data-driven insights. Data analytics tools serve as the guiding force, enabling organizations to transform raw information into actionable strategies. This guide illuminates the realm of data analytics tools, unveiling their functionalities, pivotal features, and profound impact on steering businesses toward informed decisions and strategic growth.
Understanding Data Analytics Tools
1. Defining Data Analytics Tools:
Data analytics tools encompass a suite of software and applications designed to gather, process, analyze, and interpret vast volumes of data. These tools serve as the cornerstone for extracting actionable insights from complex datasets.
2. Types of Data Analytics Tools:
The data analytics landscape spans various categories, including descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics tools. Each category offers distinct functionalities catering to specific business needs, from historical data analysis to forecasting future trends.
Essential Features
1. Robust Data Collection and Integration:
Effective tools excel in collecting and integrating data from diverse sources, ensuring comprehensive analysis. Seamless data integration allows for a holistic view, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of insights derived.
2. Dynamic Data Visualization Capabilities:
Data visualization is integral for simplifying complex data sets. Tools offering robust visualization features empower users to create interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards for enhanced comprehension and informed decision-making.
Popular Tools in the Market
1. Google Analytics:

As a frontrunner in web analytics, Google Analytics offers comprehensive insights into website traffic, user behavior, and conversion metrics. Its user-friendly interface and diverse reporting capabilities make it a go-to tool for businesses of all scales.
2. Tableau:
Tableau stands out for its powerful data visualization capabilities, enabling users to create interactive and visually appealing dashboards. Its drag-and-drop functionality and ability to handle massive datasets make it a preferred choice for in-depth analysis.
3. Microsoft Power BI:
Renowned for its seamless integration with other Microsoft products, Power BI offers robust data modeling, visualization, and business intelligence capabilities. Its intuitive interface and cloud-based services make it a versatile tool for data-driven decision-making.
4. Python and R Programming:
These programming languages serve as indispensable tools for statistical analysis, machine learning, and data manipulation. Their flexibility and extensive libraries make them invaluable for advanced data analytics.
How Data Analytics Tools Drive Business Insights
1. Strategic Decision Making:
These tools empower organizations to make informed decisions, based on insights derived from comprehensive data analysis. This strategic approach aids in formulating effective business strategies aligned with market trends.
2. Customer Insights and Personalization:
Data analytics tools unravel crucial customer behavior patterns, enabling businesses to personalize marketing strategies and enhance customer experiences. This personalized approach fosters stronger customer relationships and loyalty.
Things to Consider
1. Scalability and Compatibility:

Businesses must evaluate the scalability and compatibility of these tools with existing systems. Seamless integration ensures efficient data processing without disruptions.
2. Cost and Return on Investment (ROI):
Assessing the cost implications and potential ROI is vital. Balancing the features and capabilities offered with the associated costs ensures optimal utilization of resources.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementation
1. Data Security and Privacy Concerns:
The implementation of these tools must address data security and privacy. Robust security measures and compliance frameworks mitigate potential risks.
2. Skill Gap and Training Needs:
Addressing the skill gap by providing adequate training and upskilling programs ensures that the workforce maximizes the potential of these tools.
Future Trends
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration:
The integration of AI and machine learning capabilities into data analytics tools is evolving. Predictive analytics and automation powered by AI are shaping the future landscape of data analysis.
2. Edge Computing and Real-Time Analytics:
The rise of edge computing and real-time analytics presents new avenues for data processing. These trends promise faster insights, enabling businesses to act swiftly on emerging opportunities.
Data Governance and Compliance
1. Data Governance Framework:
Delving into the importance of establishing robust data governance frameworks to ensure data quality, integrity, and compliance with regulations.
2. Regulatory Compliance:
Addressing the significance of adhering to data regulations and compliance standards, such as GDPR and HIPAA, and how data analytics tools assist in maintaining compliance.
Cloud-Based Data Analytics Solutions
1. Benefits of Cloud-Based Analytics:
Exploring the advantages of leveraging cloud-based analytics tools, including scalability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility.
2. Leading Cloud Analytics Platforms:
Highlighting prominent cloud-based analytics platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure, and their key features.
Data Warehousing and Storage Solutions
1. Importance of Data Warehousing:
Discussing the role of data warehouses in storing and organizing vast volumes of structured and unstructured data for efficient analysis.
2. Leading Data Storage Platforms:
Exploring leading data warehousing solutions like Snowflake, Amazon Redshift, and Google BigQuery, and their functionalities in managing and processing large datasets.
Advanced Analytics and Predictive Modeling
1. Advanced Analytics Capabilities:
Detailing advanced analytics tools’ functionalities, such as predictive modeling, machine learning algorithms, and artificial intelligence for forecasting and trend analysis.
2. Predictive Modeling Applications:
Illustrating real-world applications of predictive modeling in various industries, from healthcare to finance, showcasing its role in predictive maintenance, risk assessment, and demand forecasting.
Data Analytics Tool Implementation Strategies
1. Implementation Roadmap:
Outlining a comprehensive roadmap for implementing data analytics tools, including assessment, planning, deployment, and continuous optimization.
2. Change Management and Adoption:
Addressing the significance of change management strategies to ensure the smooth adoption of data analytics tools across the organization.
Industry-Specific Data Analytics Solutions
1. Healthcare Analytics:
Exploring specialized analytics tools tailored for healthcare, focusing on patient outcomes, clinical analytics, and healthcare operations.
2. Retail and E-commerce Analytics:
Highlighting analytics solutions designed for retail and e-commerce, emphasizing customer behavior analysis, inventory management, and personalized marketing strategies.
Data Analytics for Business Intelligence
1. Business Intelligence Tools:
Discussing the synergy between data analytics and business intelligence tools, empowering organizations with actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
2. Reporting and Dashboards:
Exploring the role of reporting tools and dashboards in presenting data-driven insights in easily digestible formats for stakeholders.
Continuous Improvement and Innovation in Data Analytics
1. Iterative Analytics and Feedback Loops:
Emphasizing the importance of continuous improvement through iterative analytics and feedback loops to refine data analysis strategies.
2. Embracing Innovation:
Encouraging a culture of innovation in leveraging evolving data analytics technologies and methodologies to stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
Conclusion:
Data analytics tools are the cornerstone of modern business strategies, guiding organizations toward actionable insights. By harnessing the capabilities of these tools, businesses gain a competitive edge, fostering innovation, and driving success in today’s data-centric business environment.










