Emergency care, a pivotal component of healthcare systems worldwide, is designed to address urgent medical situations with promptness, expertise, and compassion. This comprehensive exploration delves into the multifaceted realm of emergency treatment, encompassing its core principles, specialized components, challenges, advancements, and the unwavering dedication of healthcare professionals committed to saving lives in critical moments.
Core Principles of Emergency Care
1. Immediate Response
Central to emergency treatment is the principle of immediate response. Whether it’s a medical emergency, trauma, or sudden illness, the urgency of timely intervention can significantly impact patient outcomes.
2. Prioritization and Triage
Effective emergency treatment involves prioritizing cases based on the severity of the condition. Triage systems ensure that patients with life-threatening conditions receive prompt attention, optimizing the use of limited resources.
3. Comprehensive Assessment
Healthcare professionals in emergency care conduct rapid yet thorough assessments to diagnose and understand the nature of the emergency. This process guides subsequent interventions and treatment plans.
Specialized Components of Emergency Treatment
1. Pre-hospital Care
Pre-hospital care encompasses the initial response to emergencies outside medical facilities. Emergency medical services (EMS) play a crucial role, in providing first aid, stabilizing patients, and facilitating rapid transportation to hospitals.
2. Emergency Room (ER) Services
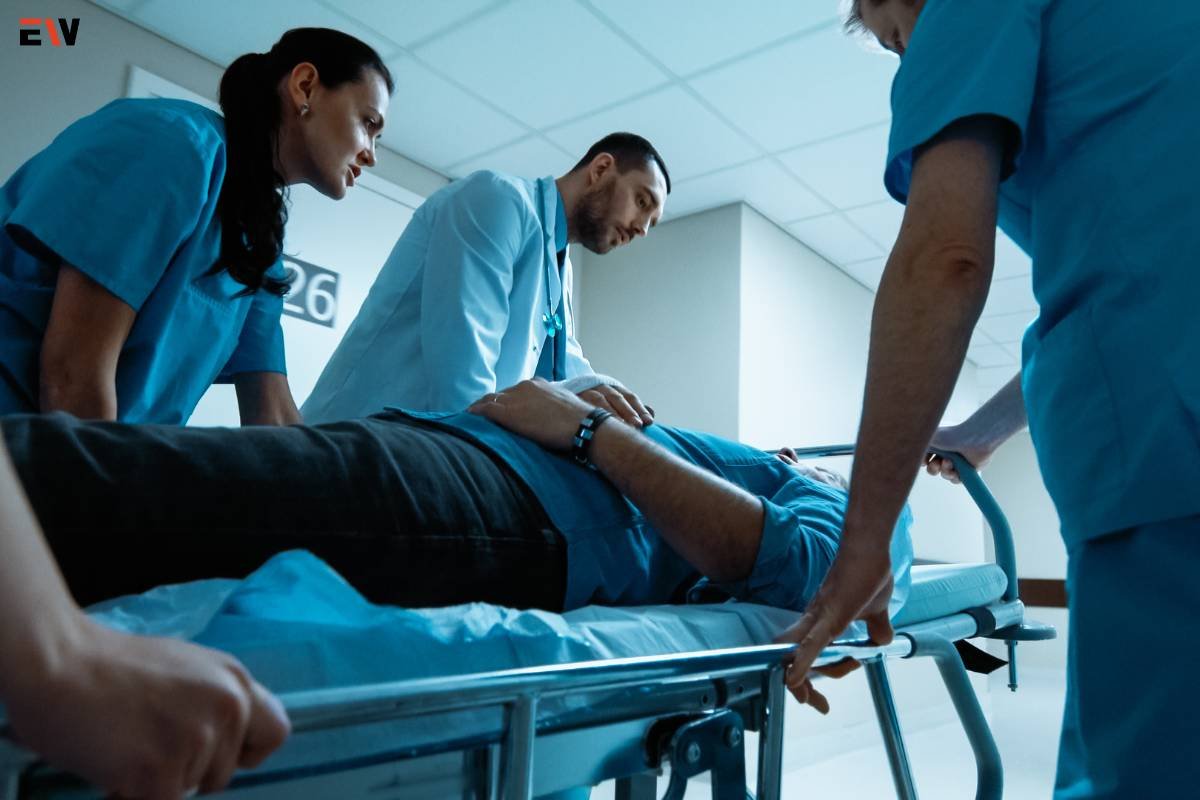

Emergency rooms serve as hubs for acute medical care within hospitals. ER teams, consisting of physicians, nurses, and specialists, handle a broad spectrum of emergencies, from trauma cases to sudden cardiac events.
3. Critical Care Units
Critical care units, including Intensive Care Units (ICUs), cater to patients with severe, life-threatening conditions. These units are equipped with specialized equipment and a skilled healthcare team capable of continuous monitoring and advanced interventions.
Challenges in Emergency Treatment
1. Overcrowding and Resource Constraints
Overcrowding in emergency departments and resource constraints pose significant challenges. Limited beds, personnel, and equipment can impede the efficiency of care delivery, especially during surges in emergencies.
2. Communication and Coordination
Effective communication and coordination are critical in emergency care. Ensuring seamless information flow between pre-hospital care, emergency rooms, and specialized units is essential for cohesive patient management.
3. Emotional Toll on Healthcare Providers
The emotionally charged nature of emergency care can take a toll on healthcare providers. Dealing with life-and-death situations, trauma, and heightened stress levels necessitates robust support systems for healthcare professionals.
Advancements in Emergency Treatment
1. Telemedicine and Triage Apps
Telemedicine and triage apps leverage technology to assess and prioritize emergency cases remotely. These innovations enhance access to timely advice, reducing unnecessary visits to emergency departments.
2. Point-of-Care Diagnostics
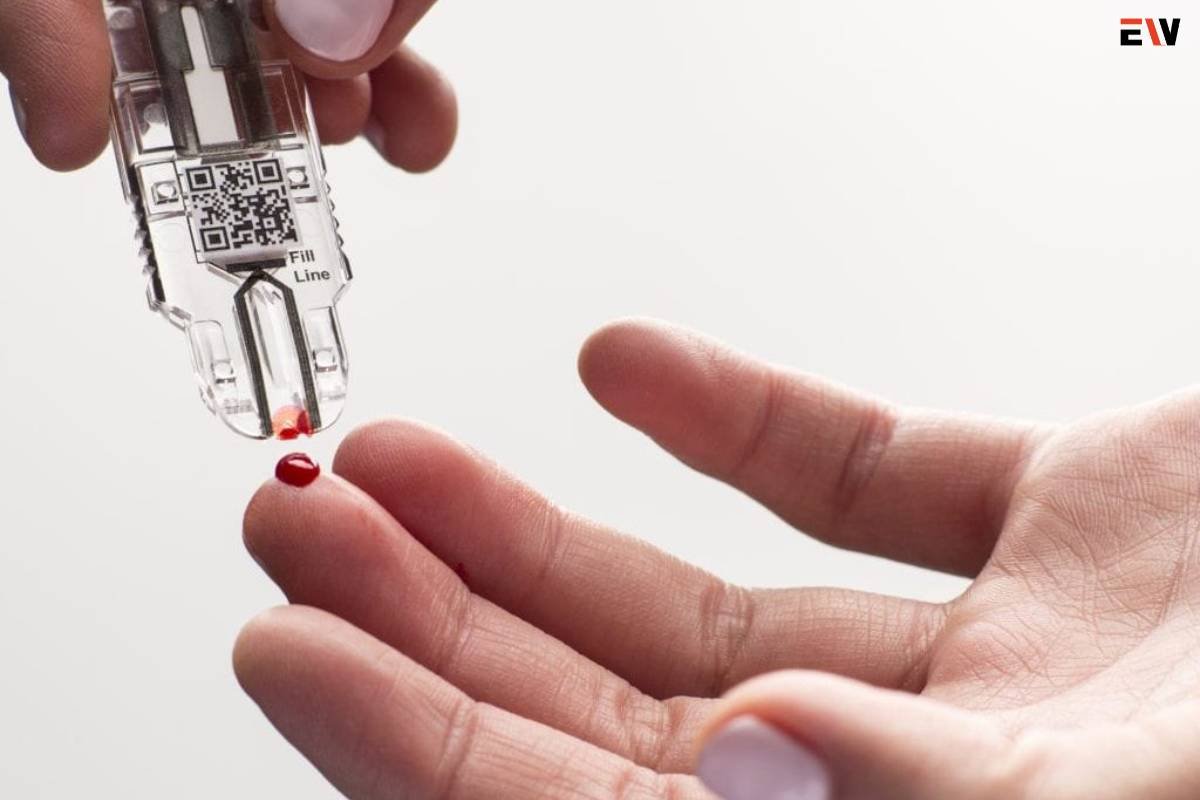
Point-of-care diagnostics enable rapid testing and diagnosis directly at the patient’s bedside. This advancement expedites decision-making processes, particularly in time-sensitive emergencies.
3. Simulation Training for Healthcare Providers
Simulation training, including virtual reality scenarios, enhances the preparedness of healthcare providers. Immersive training experiences allow professionals to practice responding to various emergencies in a controlled environment.
Humanitarian Aspects of Emergency Care (1.1%)
1. Crisis Response and Disaster Medicine
Emergency treatment extends to crisis response and disaster medicine. Healthcare professionals play pivotal roles in managing large-scale emergencies, whether natural disasters, pandemics, or mass casualties.
2. Global Health Equity
Achieving global health equity involves ensuring access to quality emergency care for all populations. Addressing disparities in healthcare infrastructure and resources is paramount in creating a more equitable emergency treatment landscape.
3. Community Education and Preparedness
Empowering communities with education on basic first aid, emergency response, and disaster preparedness is a vital aspect of humanitarian emergency care. Well-informed communities contribute to more effective initial responses.
The Human Touch in Emergency Treatment
1. Compassion and Empathy
Beyond medical expertise, compassion and empathy are foundational to emergency treatment. Healthcare providers offer not only clinical interventions but also emotional support to patients and their families during critical moments.
2. Interdisciplinary Collaboration
The collaborative nature of emergency care involves professionals from various disciplines working seamlessly. From paramedics to surgeons, this interdisciplinary collaboration ensures a holistic approach to patient care.
3. Continuous Learning and Adaptability
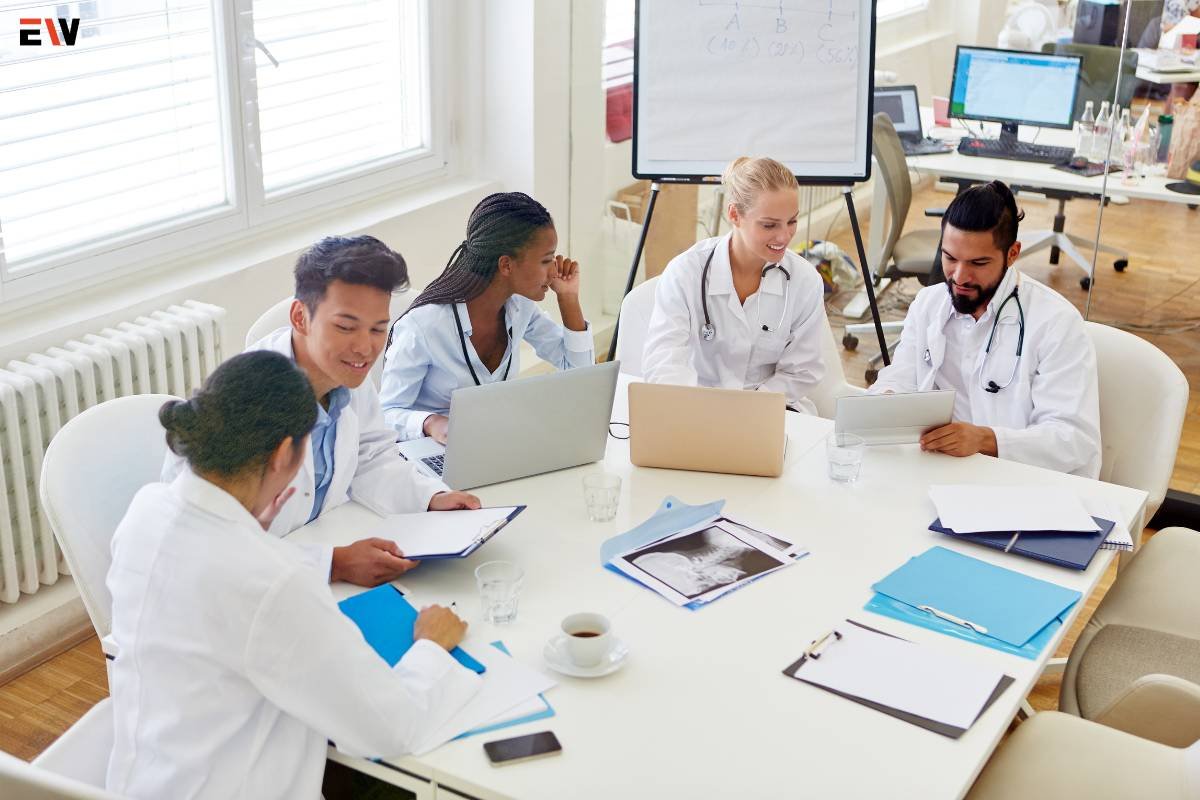

The dynamic nature of emergencies necessitates continuous learning and adaptability among healthcare providers. Staying abreast of advancements and refining protocols based on real-world experiences enhances the effectiveness of emergency care.
Future Directions in Emergency Treatment
1. AI-Assisted Triage and Decision Support
Artificial intelligence is poised to play a role in improving triage processes and providing decision support in emergency treatment. AI algorithms can analyze vast datasets to assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions.
2. Community-Integrated Emergency Response
Future emergency care models may involve greater integration with local communities. Empowering communities to play active roles in initial response and first aid can contribute to more resilient and responsive emergency systems.
3. Public Health Preparedness
Strengthening public health preparedness is crucial for effective emergency care. Proactive measures, such as vaccination campaigns and infectious disease monitoring, contribute to preventing and mitigating emergencies.
Conclusion
Emergency care stands as a beacon of hope and support during life’s most critical moments. From the immediate response of paramedics to the meticulous care provided in emergency rooms and critical care units, the field embodies a fusion of precision, compassion, and resilience. As technology continues to advance, challenges evolve, and the human touch remains irreplaceable, the trajectory of emergency treatment points toward a future where swift, effective, and compassionate interventions redefine the boundaries of what is possible in saving lives and ensuring the well-being of communities worldwide.










